What is osteoarthritis and its causes. Osteoarthritis: causes of development, symptoms, treatment
"What is osteoarthritis and how to cure it?" - this question comes up quite often. Osteoarthritis is a common disease among the pathology of the musculoskeletal system. It occurs in more than 60% of patients.
About 20% of people have symptoms of this disease. Women suffer more often. The main pathogenetic mechanism is a degenerative-dystrophic lesion of the articular cartilage, which subsequently passes to the bone. As a result, osteophytes arise, accompanied by the progression of inflammation of the synovium.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of this pathology are pain, manifested during movement. Primary osteoarthritis is accompanied by a mild clinical picture, the manifestations disappear after a short rest. With the progression of the pathology, the pain intensifies, appears with little physical exertion.

Secondary osteoarthritis is accompanied by discomfort when moving, after prolonged static load, for example, sitting. After a certain time, it goes away by itself. Occurs in the morning within half an hour after getting out of bed. With the addition of the inflammatory process, the duration of the morning "stiffness" increases. The joint has a characteristic crackle, crunch during movement.
Local status. Redness of the affected area, swelling is noted. The skin is hot to the touch.
"The manifestation of osteoarthritis of which joints are Bouchard's nodules?" - the question is relevant for patients suffering from this disease. Bouchard and Heberden's nodules, as a rule, occur at the interphalangeal joints, when the joint is displaced. Osteoarthritis of the peripheral joints can affect any joint in the human body. The joints of the lower extremities are most often affected.
Pathogenesis of osteoarthritis
Arthrosis and osteoarthritis. The basis of the pathogenesis of these pathologies is a structural disorder of cartilage at the cellular level. For the normal functioning of the connective tissue, the correct percentage in the cells of components such as collagen, proteoglycan, water, glycoprotein is necessary.
The cells that make up the cartilage are called chondrocytes. If their work is disrupted, they begin to produce matrix proteins. In view of this, depreciation deteriorates significantly.

Disruption of anabolic and catabolic interactions leads to the synthesis of inflammatory mediators:
- metal proteinase;
- cytokines;
- cyclooxygenase-2.
During the progression of the pathological process, the cartilage becomes loose. At the site of loosening, bone formations appear - osteophytes.
Due to the development of arthrosis, the surrounding tissues are involved in the process. Inflammation develops. Damage to the synovium leads to the development of synovitis.

Degrees and types of disease
Main types:
- Gonarthrosis. In this case, the knee is affected. It is difficult for the patient to stand on his feet, leaning on the sore limb. Even a small load can cause aching, throbbing pain. It is possible to alleviate the manifestations of gonarthrosis through walking.
- Coxarthrosis is a pathology of the hip joint. Because of this, a person may lose the ability to move independently. With the further development of the disease, the patient may require a wheelchair.
- Lesion of the ankle joint. This form implies that the pathology progresses as a result of an injury to the lower leg (for example, with a dislocation). With this localization, the deformation of the foot occurs.
- Shoulder arthrosis. In this situation, the pathology is accompanied by the inability to move the hand. Contractures develop.
- Elbow joint deformity. The patient loses the ability to make movements in this joint.
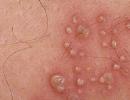
The nodular form of pathology is characteristic of gouty lesions of the interphalangeal joints. Nodules appear due to the deposition of uric acid salts.

- 1st degree. At this stage, the pain is minor. From time to time, the symptoms that appear are attributed to physical stress or overwork. The presence of the disease can be determined by examining the synovial fluid.
- 2nd degree. A distinctive feature of this stage is the occurrence of crunching and crackling in the affected limb. In addition, muscle tone may change. The marginal form is characterized by the loss of cartilage and its ossification, the lower limbs lose their motor function.
- 3rd degree. The patient cannot move independently. The joints are completely deformed. The cartilage tissue is completely destroyed.
Causes of the disease
Osteoarthritis occurs due to a number of factors, such as weight, age, concomitant chronic pathology. Experts identify the main 3 pathogenetic causes of osteoarthritis:
- dysplasia;
- injury;
- inflammation.

Dysplasia causes the progression of osteoarthritis due to the presence of congenital anomalies. There are other risk factors for osteoarthritis, due to which the development of pathology can begin:
- obesity;
- excessive physical activity;
- genetic factors (the presence of pathology in the next of kin);
- trauma;
- hormonal disorders;
- rheumatological diseases.
Injuries are the most common causes of osteoarthritis and include dislocations, subluxations, fractures, and bruises. In the absence of control of physical activity, the cartilage is injured, thinning with the transition to arthrosis.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics includes instrumental and laboratory research methods.
Instrumental
MRI. One of the most informative methods, it is possible to assess the degree of deformation, damage and inflammation of the surrounding tissues.
X-ray examination. It is carried out to diagnose pathology of the musculoskeletal system. Shooting is carried out in two projections - lateral and back-front. To determine the degree of deformation, photographs of symmetrical areas are taken. If osteoarthritis of large joints is suspected, this method is sufficient for a final diagnosis.
Arthroscopy is a diagnostic method based on joint puncture. The procedure is carried out using an LED wire that is inserted into the connection. The joint structure appears on the screen in real time. This method is used by doctors not only for diagnosis, but also for treatment. The tissues obtained as a result of the diagnostic procedure are used for histological studies.
Ultrasound. One of the safest methods. He shows the doctor an image of soft tissue. The cyst and tumor are displayed in detail on the screen.
Thermography. The method is based on diagnostics of thermal radiation of the body surface. Areas of increased temperature are foci of inflammation.

Computed tomography is a modern diagnostic method, the basis of which is the creation of several images of a specific part of the body. The information is displayed as a three-dimensional image on the screen.
Laboratory (analyzes)
This diagnostic method is used to identify which laboratory parameters are inherent in artery arthrosis, to carry out differential diagnostics, and to identify concomitant diseases.
General blood analysis. This diagnostic method gives the doctor the opportunity to correctly assess the degree of the inflammatory process. What laboratory blood parameters are inherent in osteoarthritis? Arthrosis does not have any of its characteristic features. But in the presence of concomitant inflammation, a change in blood is characteristic in the form:
- shift of the leukocyte formula to the left;
- an increase in the number of leukocytes;
- increased ESR;
- an increase in the number of lymphocytes;
- the presence or absence of thrombocytosis;

General urine analysis. It is carried out to exclude damage to the kidneys and urinary tract. The fact is that these organs can be a source of inflammation. A biochemical blood test is used for differential diagnosis.
Traditional treatment
Many people ask the question: "How to treat osteoarthritis at home?"
Traditional treatment of osteoarthritis is carried out with the help of symptomatic drugs, chondroprotectors, folk recipes, physiotherapy, exercise therapy and lifestyle changes. Clinical examination is indicated for patients with the last stages of arthrosis who need surgery.

Symptomatic drugs
You can eliminate the manifestations of the disease with the help of symptomatic drugs:
- "Paracetamol". A pain reliever that is used to relieve pain.
- "Meloxicam" or "Diclofenac" are effective in the presence of inflammation.
- Hydrocortisone. Used for severe pain.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the joints is based on the relief of pain syndrome, after which drugs are prescribed to restore the structure of the cartilage.

Modifying agents
This group includes chondroprotectors - drugs necessary to maintain the functional activity of cartilage. They have a positive effect on the metabolic process in cartilaginous tissues, inhibit the development of degenerative processes.
The main components of chondroprotectors are glucosamine and chondroitin. When treating, it is recommended to use drugs that include both substances.
Practice shows that the duration of therapy with these components is at least a quarter when using the tablet form, the course of injections is up to 2 weeks.
Regime and diet
With osteoarthritis, it is necessary to change the lifestyle, the features of which will depend on the degree of joint damage, the general well-being of the patient, and the presence of concomitant pathology. In the initial stages, when a person is physically active, a heavy load on the affected area should not be allowed.
There is no diet that slows down or stops deforming processes in cartilage tissue. However, it is recommended to change the diet for each patient. Eliminate foods that have a negative impact on the metabolic process in the body. Moreover, you should limit the consumption of salt and sugar, smoked and fried foods. Thus, eating only healthy food not only improves metabolism in the affected area, but also favors the best effect of drugs.

Osteoarthritis and arthrosis require a certain lifestyle correction, adherence to a diet, special exercises and normalization of body weight.
Thanks to remedial gymnastics, the patient can:
- eliminate muscle spasms;
- prevent muscle atrophy;
- stabilize limb movements;
- improve oxygen supply to tissues.
Therapeutic gymnastics is prescribed by the exercise therapy doctor in accordance with the characteristics of the course of the pathological process.
Physiotherapy and massage
Therapy for osteoarthritis includes physiotherapy procedures. The course and the number of procedures are prescribed by the doctor.
Massage is prescribed during the period of remission. This procedure increases the elasticity of muscle tissue and increases blood circulation, which leads to the enrichment of all joints with oxygen. Moreover, massage helps:
- stabilization of blood pressure;
- improving the patient's condition;
- accelerates metabolic and metabolic processes.

Surgery
Surgical treatment of osteoarthritis is intended for patients with the latter stage. It is used when conservative methods are ineffective. Erosive osteoarthritis is one of the most common indications for surgical treatment. Endoprosthetics is performed, the essence of which is to replace the joint.

Innovative methods
Innovative methods of treating joint diseases in osteoarthritis are characteristic of both the surgical and therapeutic aspects of rheumatology. These are intra- and periarticular injections.
In most cases, for the injection, drugs are used that are closest to the composition of the synovial fluid (for example, sodium hyaluronate). They, in turn, help to increase the elasticity and oxygen supply of chondrocytes.
As a rule, one treatment course includes 5 to 7 injections, which are administered systematically once a week. Immediately after the first procedure, the patient feels relief.
Such treatment is effective only in the initial stages. The medicine slows down the destruction of cartilage and promotes the restoration of damaged cells and tissues.
Traditional medicine recipes
How to cure osteoarthritis with traditional medicine? Traditional methods are popular among patients suffering from joint diseases. The use of this method can only help in the initial stages of pathology, since they are unable to fully replace drug treatment.
Popular recipes for traditional medicine:
- Honey, vegetable oil and mustard are mixed in equal proportions. They are heated over a fire until boiling. Leave to cool. Then it is applied to the affected area and wrapped with a cloth, cellophane. Exposure duration 2-3 hours
- A couple of tablespoons of hops, sweet clover flowers and St. John's wort, 50 grams of butter, mix and grind. Apply the resulting mix to the affected part of the body as a compress and keep for two hours.
- Heat pine oil in a volume of 10 ml to a temperature of 35 degrees. Soak the fabric with the resulting broth, sprinkle salt on it (you should get a thin layer) and apply it as a compress to the affected area for 2-2.5 hours.

Folk recipes stop the patient's symptoms only in the first stages of the disease. In the later stages, they have no therapeutic effect.
Complications of osteoarthritis
The development of osteoarthritis leads to partial or complete impairment of motor function. The consequence is disability.
If you do not start treatment of the disease in a timely manner, then the prognosis is poor, with a high probability of developing complications of osteoarthritis:
- complete deformation of the limb and the development of contractures;
- bone fractures, as well as other injuries.
The development of the consequences and complications of osteoarthritis can be prevented by timely treatment and diagnosis.
Osteoarthritis (OA) affects not only cartilage, like arthrosis, but also other tissues of the articulation. It can occur during pregnancy, children, and the elderly. Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the joints are manifested unequally, doctors prescribe a complex treatment, but the methods are selected taking into account the age of the patient, the causes of the onset and the clinical picture of the disease.
Diagnostics is the first step to getting rid of osteoarthritisThe disease is caused by degenerative-dystrophic changes in all tissues of large and / or small joints. This leads to a violation of the shape of the joint and the gradual loss of its function.
Deforming osteoarthritis (DOA) is of the following types:
- generalized;
- localized (pathology affects one joint);
- primary (the reasons that caused the development of DOA were not found);
- secondary (occurs due to trauma [post-traumatic OA] or against the background of another disease).
Generalized osteoarthritis Is a DOA that has affected two or more joints in different anatomical regions.
TO localized the species includes OA, which affects the joints of the following localizations:
- sacroiliac joints;
- shoulder ();
- elbow;
- the clavicular-acromial joint;
- hip joint ();
- knee ();
- ankle;
- spine (osteochondrosis);
- peripheral joints (wrists, hands, feet, other areas).
There is also "patellofemoral pain syndrome". It occurs when OA destroys the joint that consists of the upper edge of the patella and the femur. Experts consider this syndrome a harbinger of gonarthrosis.
OA is a common disease that can occur at any age. Guys with third or fourth degree osteoarthritis are not recruited into the army. In the first and second stages of OA, the conscript is assigned a category B and is given a reprieve.
 A delay for up to a year is given for osteoarthritis of 1 to 2 degrees
A delay for up to a year is given for osteoarthritis of 1 to 2 degrees Which doctor treats osteoarthritis
If the patient decides to use folk remedies, then you need to contact a phytotherapist in order to choose the right medications that help with joint diseases.
You need to get advice from the following specialists:
- orthopedist;
- rheumatologist;
- traumatologist;
- orthopedic surgeon.
It is advisable to consult a nutritionist and physiotherapist in order to choose the right diet, exercise, physiotherapy. Women with osteoarthritis, who have confirmed pregnancy, should be observed not only by a gynecologist-obstetrician, but also by a rheumatologist.
Where do you get your disability?
It is necessary to contact the medical and social expert commission. Doctors of the MSEC will assess the patient's health status to assign him disability groups 1, 2 or 3, which depends on the presence of an endoprosthesis, rapid progression of OA or its frequent exacerbations. To obtain a disability, a patient must present to experts radiographs, an outpatient card with specialist records, and hospital discharge.
Factors provoking the onset of osteoarthritis
The reasons for the development of DOA can be persistent microtrauma, dysplasia and inflammatory processes in the structures of the joint, which disrupt its biomechanics.
Often, the following pathological circumstances are capable of provoking the onset of DOA:
- obesity;
- endocrine diseases;
- diseases of the musculoskeletal and muscular system;
- estrogen deficiency and hormonal imbalance;
- genetic disorders.
- excessive stress on the joints.
Sometimes the impetus for the onset of the disease is given by non-compliance with the drinking regime. Due to the lack of fluid, the articular cartilage loses its elasticity and begins to crumble. Torn off fragments during movement cause intra-articular inflammation, which is the main cause of pain in DOA.
Additionally, the following risk factors are distinguished:
- over 60 years of age;
- hereditary predisposition;
- the presence of chronic joint diseases;
- undergone surgery on the joints;
- physical overload.
Osteoarthritis manifestations
Pathology has four degrees of severity, develops slowly. Often in children and adults, the disease manifests itself in different ways.
Initial symptoms are often confused with fatigue, as aching pains disappear after rest.
General subjective signs of osteoarthritis:
- stiffness in the area of the damaged joint after sleep;
- crepitus (crunching, crackling or creaking is heard during movement);
- increased muscle fatigue;
- over time, the pain becomes constant, and pain relievers do not help.
The progression of the disease is confirmed by symptoms such as periodic exacerbations of the disease and gradual deformation of the joint. In deforming OA, pain syndrome is associated with constant inflammation of the articular structures, damage to bone and cartilage tissue during movement. The range of motion in the joint decreases due to the proliferation of osteophytes and the gradual destruction of the osteochondral elements.
 In osteoarthritis, joint deformity is eliminated by surgical methods
In osteoarthritis, joint deformity is eliminated by surgical methods Objective signs
Each degree of DOA has a different radiological and arthroscopic picture. Using X-rays, specialists assess the extent of joint damage.
X-ray signs of osteoarthritis:
- In the first degree, there are minor nonspecific changes.
- In the second degree, the picture shows some narrowing of the joint space, the formation of individual osteophytes. Joint deformation is negligible.
- The third degree is manifested by multiple bone growths. The joint gap is moderately narrowed.
- At the fourth stage of development of OA, the image shows a significant deformation of the bone, a sharply narrowed joint space. Osteophytes reach large sizes.
Visual changes in the damaged joints are observed: the joint increases in size, tubercles are felt or protrude under the skin, curvature of the fingers and feet are visible.
 Using the arthroscope camera, doctors assess the condition of the intra-articular tissues
Using the arthroscope camera, doctors assess the condition of the intra-articular tissues Arthroscopic signs of OA (Outbridge classification):
- First degree: no or minor visual changes.
- In the second degree, the heterogeneity of the cartilage is visible. There are tears, cracks, patches or other defects on its surface.
- Third degree: cartilage stratification appears, a "fringe" is formed along its edge. The severity of defects of the previous stage is aggravated.
- At the fourth degree, the cartilage is destroyed so much that the bone is exposed, large erosions appear, congruence is disturbed (the correspondence of the elements of the articular surface to each other).
How to identify the disease
During the initial examination, the doctor listens to the patient's complaints and examines him carefully. Then, directions are written for general and biochemical blood tests, taking synovial fluid for laboratory research.
Hardware diagnostics of DOA includes the following methods:
- arthroscopy;
- x-ray;
- magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography;
- thermography.
 In the process of diagnosis, doctors exclude diseases that are similar in terms of symptoms.
In the process of diagnosis, doctors exclude diseases that are similar in terms of symptoms. Doctors rule out possible joint diseases that have similar clinical manifestations. Primarily carried out differential diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and osteoarthritis.
The difference between RA and DOA
- In RA, at the very beginning of the disease, inflammation is manifested by reddening of the skin, swelling of the joints, and pain. With the development of DOA, these symptoms appear much later.
- With RA, the work of internal organs is disrupted, rheumatic nodules appear on the fingers. Osteoarthritis does not cause such changes.
- In rheumatoid arthritis, x-rays show osteoporosis, not osteosclerosis.
With RA in the blood, laboratory assistants detect an acceleration of ESR and the presence of rheumatoid factor. If an increased urea content is detected, then the person may have a psoriatic type of arthritis. The difference between osteoporosis and osteoarthritis is that OA destroys only the articular tissues, while osteoporosis is accompanied by a loss of bone tissue of various localization.
What can be the wording of the diagnosis:
- Generalized form of arthrosis: bilateral coxarthrosis 3 degrees, gonarthrosis of the right knee 2 tbsp.
- Local osteoarthritis: right-sided omarthrosis complicated by synovitis.
Treatment methods
Therapeutic methods are selected individually. All methods should be aimed at stopping degenerative processes in the joints and maintaining their functionality.
Pharmacotherapy
Medical treatment is prescribed prior to arthroplasty. Medicines eliminate symptoms, slow down the progression of the disease.
 Endoprosthetics completely restores the working capacity of the limb
Endoprosthetics completely restores the working capacity of the limb For the treatment of osteoarthritis, the following drugs are used:
- analgesics (Baralgin, Analgin, Tramadol, Dexalgin);
- NSAIDs (Aceclofenac, Naproxen, Meloxicam, Nimesulide, Etoricoxib, other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
- chondroprotectors (Elbona, Glucosamine sulfate, Structum).
In addition, agents are prescribed for the local treatment of stage 1–3 OA.
Medicines for osteoarthritis for external use - ointments, creams, gels. The most commonly used drugs are:
- Brufen;
- Veral;
- Dicloran;
- Ketonal;
- Enelbin Paste;
- Artrosenax;
Disease 2-3 degrees should be treated, also using intra-articular injections. Injections are done under ultrasound control to see the depth of penetration of the needle into the joint cavity.
In OA, the following medications are administered into the joint:
- hyaluronic acid preparations;
- long-acting glucocorticosteroid hormones;
- plasma platelet-rich injection fluids.
 Intra-articular injections of Autoplasma ─ a new method of treating osteoarthritis
Intra-articular injections of Autoplasma ─ a new method of treating osteoarthritis For pregnant women, an effective medicine is selected by the attending physician. Intra-articular injections, physiotherapy, mud therapy, folk external remedies (most!) Are considered safe for the fetus. It is dangerous to use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs without consulting a doctor.
Operations are indicated for the second to fourth degree of the disease. The cheapest surgical intervention is arthroscopic debridement.
 Arthroscopy is performed to remove cartilage fragments and excess synovial fluid
Arthroscopy is performed to remove cartilage fragments and excess synovial fluid Debris, which consists of pathological synovial fluid, fragments of cartilage and fragments of osteophytes, is removed from the joint cavity with an arthroscope. Less commonly, periarticular osteotomy and endoprosthetics are performed. Each procedure has its own contraindications, which the attending physician warns about.
 To eliminate joint deformity, bone correction is done
To eliminate joint deformity, bone correction is done Drug-free treatment
These therapies include physiotherapy, massage, exercise therapy, and diet. With their help, they normalize metabolism, eliminate inflammation, relieve pain, develop a deformed joint.
Modern methods of physiotherapy:
- UFO-irradiation;
- infrared laser therapy;
- UBCH-therapy;
- CMB-therapy;
- magnetotherapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- balneotherapy (hydrogen sulfide and radon baths).
 The sanatoriums for the treatment of osteoarthritis combine the methods of balneotherapy and exercise therapy
The sanatoriums for the treatment of osteoarthritis combine the methods of balneotherapy and exercise therapy Massage scheme:
- First, the tissues of the joint are warmed up with stroking and rubbing movements.
- During the massage, circular movements are performed more intensively, with pressure, stretching the periarticular muscles. It is necessary to avoid the appearance of pain during the procedure.
- Finish the session with light stroking.
Physiotherapy
Daily gymnastics is a mandatory wellness procedure. Physiotherapy exercises can be combined with swimming, yoga, but you can not run, do aerobics. Patients begin to engage in exercise therapy under the supervision of a specialist, and later exercise is done at home after sleep. The set of exercises recommended for joint diseases, see the video.
Diet
Nutrition should be selected on an individual basis, guided by the recommendations of a nutritionist. This is especially true for the treatment of children, pregnant women and the elderly.
The following general principles of therapeutic nutrition for osteoarthritis have been developed:
- the calorie content of food should correspond to the energy consumption of a person;
- lack of strict diets;
- fractional food intake;
- restriction in the diet of salt, simple carbohydrates, animal fats;
- eating fiber-fortified foods.
You can not eat refined fats, lard, fatty meat, canned food, fast food.
What vitamins are needed for DOA and what foods do they contain? You need to eat the following foods:
- C: citrus fruits, rose hips, melon, cabbage, tomatoes;
- D: seafood, eggs;
- β-carotene: pumpkin, asparagus, apricots.
It is also important to include in the diet foods containing the following beneficial substances:
- omega-3: flax seeds, nuts;
- bioflavonoids: green tea, apples, broccoli, lingonberries, blueberries;
- calcium: fermented milk drinks, cheese, cottage cheese.
There is a special calcium diet. Eating foods with a high Ca content will strengthen bones, improve cell metabolism, and accelerate the regeneration of joint tissues.
 What foods are consumed with a calcium diet
What foods are consumed with a calcium diet How to treat at home
After consulting a doctor, you can purchase medical devices for the treatment of osteoarthritis at home. Experts often recommend Stiotron, Orion, Milta.
At home, you can carry out not only physiotherapy, but also apply the methods of alternative therapy. It is imperative to coordinate treatment with a doctor. Decoctions of medicinal herbs inside, medical compresses, rubbing and other folk remedies for external use help well.
Conclusion
In all people, the pathogenesis of OA proceeds according to the same scheme, but the symptoms of osteoarthritis of the joints can manifest themselves in different ways depending on age, gender, health status. Treatment will be effective if patients strictly adhere to medical prescriptions. It is necessary to use joint fixators, engage in physiotherapy exercises, eat right, and receive spa treatment. It must be remembered that the best remedy for the progression of pathology is the prevention of exacerbations.
Osteoarthritis: what it is, what are its causes and symptoms, what treatment methods exist - the answers to these questions will interest many people, especially in old age.
Joint diseases and osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is called deformans osteoarthritis, which is a common type of arthritis. The disease is chronic, i.e. damage to the bone and articular structure of the human skeleton occurs slowly and irreversibly.
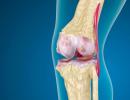
What is osteoarthritis? This is the destruction of muscle tissue in the main joints, which include those that are most susceptible to stress: knees, hips, spine and hands.
Most often, this disease affects men and women after 45 years, but every year more and more cases of the disease are recorded among younger people.
Articular cartilage is a fairly strong material that acts as a shock absorber during impacts, ensuring smooth sliding of adjacent joint bones. When it is destroyed and erased, the friction of surfaces increases, pain occurs, and deformation occurs.

Synovial fluid is a thick lubricating substance that reduces friction and wear on the articular surfaces. As the disease progresses, it becomes less dense and elastic.
There are 2 types of the disease: primary and secondary osteoarthritis. The first develops with natural wear of the cartilage tissue as a result of human aging, and the second - under the influence of external negative factors.
Osteoarthritis causes
Factors affecting the increase in the likelihood of a disease in humans:
- hereditary predisposition due to a gene defect that is responsible for the correct formation of cartilage tissue, damage to it and causes problems with joints - this is the most significant factor affecting the onset of the disease in 30% of cases;
- obesity - contributes to the appearance of diseases of the knee and hip joints due to the heavy load on them;
- injuries, especially in athletes, increase the risk of illness in those areas where injuries occur (back, knees, etc.);
- great stress on the joints due to professional activities.
The main reason for the development of osteoarthritis of the joints is a slow metabolism, which is why changes in the cartilage tissues occur. In addition, modern scientists identify other reasons for the development of the disease:
- age-related changes in the human body, in which there is a decrease in tissue elasticity;
- excess body weight and overloading of joints and bones also contribute to destruction;
- the influence of toxins in viral diseases, with an improper lifestyle (alcohol and smoking abuse);
- endocrine disorders in the body: diabetes, menopause in women, hormonal disorders in diseases of the thyroid gland, etc.;
- diseases of the vascular system, atherosclerosis, changes in the walls of the arteries.
Osteoarthritis: symptoms
The manifestations of joint disease develop gradually, which is why the patient may not immediately guess about his problem. In the absence of treatment, degeneration of cartilage tissue occurs and the subsequent deterioration of the patient's condition. Therefore, one should pay attention to the appearance of pain in the joints immediately in order to start treatment as quickly as possible and slow down the development of the disease.
The main symptoms of osteoarthritis are:
- Joint pain during movement, which at first does not bother a person much, because in a calm state they are not.
- As the disease progresses, pain appears after a period of rest or from severe exertion. If, during an exacerbation at the initial stage, treatment is not started on time, then the disease progresses.
- There is an overgrowth of bone tissue in the fingers, etc., soreness is felt even with little activity.
- Swelling of the joints due to accumulation of synovial fluid.
With a sharp movement, the patient can hear a click in the area of the sore joint - crepitus, which is more pronounced in cold and damp conditions.
Over time, periods of exacerbation of the disease begin to become more frequent, joint mobility decreases, the patient may even completely lose motor function. It is caused by degenerative processes in the tissues. External changes also occur: redness of painful areas and an increase in the volume of the articular cups.

At the next stage in the development of osteoarthritis of the joints, fluid accumulates in the cavity of the joint capsules, which often contributes to an increase in body temperature in the affected area: the joint swells and is hot to the touch. The proliferation of tissue over time leads to compression of the nerve endings around the joints, which reduces sensitivity, possibly numbness and pain relief.
Osteoarthritis manifestations depending on the affected area
Symptoms and treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint or hip differ only in the location of pain during movement, and in the area of cartilage damage.
So, with osteoarthritis of the knee joint, pain is manifested when bending and extending the knees, with a lesion of the hip - in the thigh area and given to the groin area, with a disease of the spine - localized in the lumbar zone or in the neck. Often soreness is associated with a change in weather or climate, stress on the sore joint.
In severe cases, with hyper-proliferation of articular tissues, blood vessels are compressed, the consequences depend on the location of the diseased joints. In case of damage to the spinal column, compression of the esophagus is likely, which will lead to dysphagia, with the growth of joints in the neck, dizziness and severe headaches are possible.
According to scientists, 15% of the world's population has various forms of osteoarthritis. After 35 years of age, the risk of developing the disease is 50%, and after 50 years it rises to 75%, over 70 years - already 90%.

What it is - "osteoarthritis" with age learns almost every person as his body ages, and in the presence of negative factors or excessive stress - even earlier.
Diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis
The best way to diagnose osteoarthritis is a complete examination of the patient in a hospital in a hospital setting. This allows not only to make the correct diagnosis, but also to develop the most effective treatment plan.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of analyzes and studies:
- general examination and description of symptoms;
- clarification of the location of the pain;
- X-ray of the affected area, ultrasound examination, if necessary, the doctor prescribes an MRI - according to the images obtained, changes in the joint can be traced;
- fluid is made (arthrocentesis), its biochemical analysis is carried out;
- blood tests.
Based on the data obtained, the doctor gives an opinion on the severity and degree of osteoarthritis, on the use of painkillers, and an individual treatment method is developed.
Therapies
The disease is chronic, therefore the main goal of doctors is to slow down the processes of joint deformation and the further development of the disease.
The goal of the initial stage of osteoarthritis treatment is to reduce pain during periods of exacerbation, for which pain relievers are prescribed to help restore joint mobility. It should be borne in mind that frequent use of such drugs may be accompanied by gastrointestinal diseases or gastritis, and they will not be able to stop the degenerative process.
The most effective treatments:
- weight loss of the patient, which implies a special diet;
- therapeutic exercises and physiotherapy procedures;
- taking medications for pain relief (pills, etc.);
- the use of adaptive devices (orthopedic shoes, knee pads, splints, etc.);
- removal of joint fluid, the introduction of drugs into the diseased joint.

The main goal in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint and other affected areas is weight loss and diet, as well as regular exercise, swimming and cycling are very useful. In combination with physiotherapy, this will strengthen the muscles, ligaments and tendons near the joint and normalize the process of supply of beneficial nutrients to the tissues. Thermal procedures and compresses help to relieve pain. In case of incorrect posture, as one of the causes of the onset of the disease, its correction is necessary.
If the disease progresses, then bandages and splints will help get rid of the pain, which immobilize the affected joint. If the above methods do not help, then surgical intervention is recommended.
Medicines

With osteoarthritis, treatment should be comprehensive, aimed not only at relieving pain, but also at eliminating the causes of the disease, and restoring cartilage tissue. To do this, apply:
- in tablet form: Tylenol, aspirin, Ibuprofen, Celebrex, paracetamol, etc .;
- ointments and creams are applied directly to the area of the sore joint;
- chondroprotectors of the 3rd generation - are prescribed to protect the cartilaginous tissue from destruction;
- drugs for molecular-structural restoration of cartilage tissue - improve joint mobility;
- injections into the affected joint are made with special preparations in cycles of up to 3-5 pieces per week, they are used only for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint.
Surgical methods
Endoprosthetics is the most widespread and rather expensive method of treatment. replacement of a joint with an artificial one. Such a prosthesis cannot completely replace the motor abilities of a natural one, but it allows you to remove pain. Most often, replantation of the knee and hip joints is done.
There are also other surgical methods:
- cleansing the joint with an arthroscope: piercing the skin in several places and polishing the damaged cartilage, is done only in the early stages, but it is considered an insufficiently effective procedure;
- osteotomy is an operation designed to restore the function of a joint damaged by a disease for some time.
Knee osteoarthritis and its treatment
The knee joint is most often affected by this disease, because a great load is placed on him when walking and other movements.
The symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee joint are similar to those already listed: pain in the knee when flexing and extending, especially when walking up the stairs. As the condition worsens, stiffness is felt, movement becomes difficult, and swelling appears. The pain is usually worse in the morning, after rest, or after intense exertion, while standing on your knees.
During the examination, an x-ray shows a narrowing of the space between the joints of the affected knee.

The attending physician, in accordance with the degree of the lesion and the symptoms of osteoarthritis, prescribes treatment for the patient in the form of pain relievers, recommends therapeutic and restorative exercises that will help strengthen the muscles of the legs and improve flexibility.
In case of severe pain, special knee pads and splints can be used, which, according to patients' testimony, help to reduce pain syndrome and allow more active movement.
With this method, 2 types of tires are used:
- unloading, which reduces the load on the diseased area;
- supportive - allows you to evenly distribute the load on the joint.
One of the methods of treatment is the use of dietary supplements, food supplements containing aminoglucose and chondroitin sulfates. These substances are natural components of articular cartilage. Supplements are made from animal products or synthetic substances and are quite effective in the early stages of osteoarthritis. To achieve a tangible effect, you must complete a full course of medication for at least three months. This will help reduce swelling and inflammation in the joint, and improve the patient's physical activity.

It should be borne in mind that dietary supplements can interact with medications prescribed by a doctor, therefore, they must be warned about taking them.
Knee injections
One of the methods to help relieve pain and improve the condition is an injection into the knee joint. In this case, various medications can be used:
- Corticosteroids, cortisones are hormonal drugs that have analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. The disadvantage of their use is the short duration of action and possible side effects, up to the destruction of the joint with too frequent procedures.
- Hyaluronic acid injections. They help to strengthen the astringent function of the synovial membrane and replenish the missing fluid in the knee joint, this method is effective in the early stages of the disease, if other drugs do not help.
- Sodium gold hydrochloride injections are one of the popular treatments for arthritis.
Traditional methods of treatment
Various herbal preparations and tinctures help reduce pain and stop the destruction of articular cartilage. They are effective in the complex treatment of joint osteoarthritis.

A popular folk recipe for oral administration: a mixture of elderberry flowers, juniper, nettle leaves, horsetail herb, calendula, willow bark in equal proportions. At 2 st. l. the mixture is added 1 liter of boiling water, you need to insist for 12 hours, and then strain. The infusion should be consumed ½ glass several times a day, the course of treatment is 2 months.
Topical compresses and ointments help reduce pain, improve blood circulation, and relax muscles and ligaments around the sore joint.
Most popular recipes:
- Mix 2 tbsp. l. castor oil with 1 tbsp. l. turpentine. Rub the joint with this solution twice a day.
- The compress is made from chopped horseradish root, which is steamed over low heat, then the finished mass is placed in cotton cloth and applied to the sore joint.
- Infusion of dandelion flowers. The bottle is filled with flowers, then alcohol or cologne is added to the top, insisted for 1 month. and filter. Every evening you need to rub your sore knees with dandelion infusion for a month, in especially severe cases it can be longer. At the same time, it is recommended to chew several times daily. You can store the infusion at room temperature.
- A mixture prepared from 5% iodine and 10% ammonia, May flower honey, glycerin and medical bile (in equal proportions) is infused for 10 days in the dark. Before use, it should be warmed up in a water bath. It is applied in the form of a compress on the joint at night, the knee is wrapped on top of the knee with polyethylene and a woolen scarf.
- Soak a linen cloth with celandine juice and apply on a sore knee for 40-60 minutes, then grease with sunflower oil.
It should be remembered that folk remedies are auxiliary treatments for osteoarthritis, and are used in combination with medications prescribed by the attending physician.

Knowing what consequences the lack of treatment for osteoarthritis can lead to, what it is and how to treat it, you need to carefully monitor your health, especially in old age, when the likelihood of the disease is maximum.
Osteoarthritis is a group of diseases with different etiology, but similar in morphological and clinical manifestations, sooner or later ending in complete loss of articular cartilage and damage to all elements of the joint. The incidence of osteoarthritis increases sharply with age - almost 50% of people over 55 have clinical and radiological signs of this disease. Osteoarthritis often affects young people, being one of the most common causes of temporary disability, worsening the quality of life and causing considerable financial costs. Over the past 6 years, the prevalence of this disease has increased by 135%.
Etiology (causes of development) of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is characterized by the gradual destruction of the articular cartilage.If the cause of the disease could not be identified, then osteoarthritis is usually called idiopathic, or primary. The main factors initiating the development of primary osteoarthritis are:
- hereditary predisposition (change in the genotype, due to which the ability of cartilage to withstand mechanical stress is reduced to one degree or another);
- regular physical stress.
Some external and internal factors can provoke the development of primary osteoarthritis.
External factors:
- regular overload of the joints (playing sports, working on the legs);
- joint injuries and microtraumas;
- excessive joint mobility;
- unbalanced diet;
- intoxication (nitrates, herbicides, heavy metal salts);
- viral infections.
Internal factors:
- congenital disorders of the joint structure;
- hereditary diseases of the osteoarticular apparatus;
- overweight;
- violation of posture;
- circulatory disorders, both general and local;
- endocrine disorders;
- concomitant chronic diseases, including arthritis, previously transferred.
The causes of secondary osteoarthritis can be:
- inflammatory processes in the joints (rheumatoid arthritis, atritis with SLE, tuberculosis, reactive arthritis);
- joint injuries;
- degenerative-necrotic processes in the joints (aseptic bone necrosis, Perthes disease).
Despite the variety of etiological factors, the main reasons for the development of osteoarthritis are:
- trauma;
- dysplasia;
- inflammation.
Pathogenesis of the disease
The causal factors of osteoarthritis trigger the processes of early aging of the articular cartilage - the metabolism in the cartilage tissue slows down, as a result of which the cartilage loses its elasticity, becomes rough, cracks appear on it, exposing the underlying bone.
The consequence of reduced amortization is the compaction of the articular surfaces of the bones and the formation of cysts, areas, sclerosis.
Thanks to compensatory processes, cartilage grows outside the joint, forming marginal osteophytes.
The end result of the above processes is the complete destruction of cartilage and dysfunction of the affected joint.
Osteoarthritis symptoms
- Dull, deep joint pain associated with movement. In the initial stages, the pain is not intense, occurs with a pronounced load on the joint (often when climbing stairs) and disappears after rest. As the disease progresses, the pain intensifies, occurs with minimal exertion and practically does not go away at rest.
- The pains that appear at the first steps of the patient are the so-called starting pains. When the patient "disperses", the pain temporarily stops, but with continued load on the joint, it reappears.
- Morning stiffness in the affected joints lasting up to 30 minutes. In the case of the addition of an inflammatory process, the time of morning stiffness is lengthened.
- Crepitation (creaking, crunching, or crackling) in the affected joint during movement.
- Limitation of joint mobility.
- Sudden "jamming" of the joint or "blockade" pain (sharp pain with the slightest movement).
- As the disease progresses, the affected joint deforms, so-called Heberden's and Bouchard's nodules appear in the interphalangeal joints.
This disease can affect any joints, but most often those of them that experience the greatest stress during a person's life are involved in the process - large joints of the lower, less often upper limbs, small joints of the hands.
Diagnostics
 On the roentgenogram of the joint affected by osteoarthritis, the essence of the joint space and bone growths along the edge of the articular surfaces - osteophytes - are found.
On the roentgenogram of the joint affected by osteoarthritis, the essence of the joint space and bone growths along the edge of the articular surfaces - osteophytes - are found. The preliminary diagnosis is established on the basis of the patient's complaints and the data of an objective examination (joint deformity, pain on palpation, limitation of range of motion, crepitus). To confirm the diagnosis, an X-ray is taken (in the picture of the joint, a narrowing of the joint space is noticeable, marginal bone growths are osteophytes, at a later stage - flattening of the articular surface of the bone).
In the general analysis of blood, there are usually no changes. The only exception is osteoarthritis with the phenomenon of reactive synovitis (inflammation of the joint capsule) - in this case, in the blood test, an ESR increase of up to 20-25 mm / h, a slight leukocytosis is possible.
Treatment
Specialists have developed a special algorithm for the treatment of osteoarthritis, which includes 3 stages. So.
- Elimination of mechanical factors affecting the joint: unloading the affected joint, weight loss, using a cane while walking, wearing a corset, orthopedic shoes.
- Physiotherapy: hydrotherapy, thermal procedures.
- Exercise therapy: posture correction, exercises without stress on the joints.
- Local: gels, creams, ointments.
- When osteoarthritis occurs for the first time or with inflammation of the joint - NSAIDs in tablets, injections or rectally.
- Chondroprotectors.
- With persisting signs of inflammation - glucocorticoids in the joint.
- If conservative treatment is ineffective - joint replacement.
Prophylaxis
The main measures to prevent the development and cover the progression of osteoarthritis are:
- reduction in excess body weight;
- prevention of injuries;
- timely correction of congenital joint diseases;
- adequate physical activity.
Which doctor to contact
In the early stages, osteoarthritis is treated by a rheumatologist, then the help of an orthopedic traumatologist is needed. In addition, a physiotherapist, a specialist in physiotherapy exercises and massage can alleviate the patient's condition. A patient with osteoarthritis and overweight needs to consult an endocrinologist and a nutritionist, because obesity leads to a rapid progression of the disease.
About arthrosis of the knee joint in the program "On the most important thing."
Very often you can hear from older generations of people complaints of very tangible pain in the joint areas. As a result, many of us are unable to consider the severity of the consequences of this disease. About fifteen percent of these health complaints are the first signs of a terrible disease called osteoarthritis. What kind of disease is this, how it needs to be treated, how is it capable of proceeding in the body as a whole. Let's take a closer look at all these issues with you in more detail.
Detailed diagram of the development of osteoarthritis:
- At the junction of the bone and cartilage, the latter becomes thinner.
- Through the destruction of the cartilage, peculiar pieces are separated from it.
- A disease called osteoarthritis develops.
Osteoarthritis is a whole complex of diseases that differ from each other in consequence - causal factors, but generally lead to a single outcome - the origin of irreversible and irreparable changes in the articular parts of the human body.
Cartilaginous areas in the joints are considered to be some kind of shock absorbers or pads that reduce the coefficient of friction between the bone part and contribute to the mobility of any part of the body. The cartilaginous parts in a healthy body appear rather smooth in structure. When the disease affects parts of the body, the cartilage structure tends to be disrupted in a dramatic way. The surfaces of the cartilage are somewhat rough, without much evenness. In some situations, destruction can occur directly to the bone.
Based on laboratory studies by experienced specialists in the medical industry, it can be argued that about twenty percent of the inhabitants of the entire planet as a whole suffer from osteoarthritis. It should be noted that often, for the first time, a person begins to feel the full severity of this disease at the age of about forty-five years.
The older the patient, the greater the risk of developing osteoarthritis. Moreover, at an older age, treatment will be much more difficult, and the symptoms of the disease will be very bright. But it should not be fully asserted that only the elderly are ill with this disease. With a high probability, young people can also get osteoarthritis. The causes of osteoarthritis disease can be the large weight of the patient, not a rational lifestyle, disposition to this disease at the genetic level.
The symptoms of the disease will be as follows:
About one third of patients suffering from osteoarthritis say that their pain in the joint area begins with stress on them and ends when the body is resting. With such complaints, first of all, you need to pay special attention to the skin around the joints in a qualitative way. If the skin is warm and some redness is visible on it, then this is probably not osteoarthritis. Experienced doctors will be able to make more accurate assumptions of diagnoses in a specialized medical clinic, who can easily distinguish osteoarthritis from other diseases. But if the pain in the joints increases after physical exertion, then this is osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis causes
We have already noted that osteoarthritis is a chronic disease, where articular cartilage and bone adhesion are degeneratively changed. Because of this, very severe pain occurs in the joints, the joints become stiff.
Experienced medical professionals believe that osteoarthritis is a direct sign that a person is aging. But today, even a young person under the age of thirty can get sick with this ailment. The reasons for the spread of the disease can be very diverse.
Let's take a closer look at the causes of osteoarthritis:
Today, the most common joint disease in the human body is osteoarthritis. All this happens due to wear or damage to the cartilage tissue, which is caused by various types of inflammation, intoxication. Osteoarthritis can develop in the body for a very long time. The cartilage in the affected joint without special lubrication will collapse, bringing unbearable pain to its owner.
Primary arthrosis occurs in the event of a violation of the cellular composition, which synthesizes the cartilage membrane. As a result, the cartilage of the joint becomes thin due to excessive friction and eventually cracks.
Osteoarthritis symptoms
A disease called osteoarthritis is very scary and destructive for the body. Osteoarthritis includes arthrosis of the hip joint, arthrosis of the spine, knee joints, elbow joints, and cervical spines. The symptoms of these diseases are identical with each other and have a number of specific elements.
The signs of osteoarthritis include the following:
- The joint will be significantly deformed during the course of this disease in the human body.
- By its nature, the destruction of the joint will have a global appearance.
The essence of the disease proceeds as follows in the patient's body. Each joint contains cartilage that facilitates normal limb movement. These cartilages allow bones to work without any friction against each other. We can say that cartilage can allow bones to slide in places of their contact. Over time, the cartilage tends to lose a fraction of the necessary fluid, which all this time served as a lubricant. Without fluid, all cartilage is prone to cracking. After the cartilage has cracked and split, the bones begin to work by rubbing against each other. The result is a kind of growths, called osteophyte in nature. This is a very painful sensation.
So, you should consider the list of symptoms that manifest themselves with osteoarthritis of the hip joint, spine, knee or elbow joint.
This symptomatology will express the dependence of the progression of the disease in the human body as a whole. During the symptoms of this disease:
- Significant joint pain under various loads. The pain can flare up both during rest and when the load on the body increases.
- Muscles may atrophy if osteoarthritis is not treated at all.
- There is an effect of stiffness when moving or moving parts of the human body.
- When a sick person walks, he will limp. A person with osteoarthritis will not be able to take large steps when walking.
- As the disease progresses, one can observe the fact that the limbs begin to differ in length. For example, one leg may be longer than the other, etc. The affected limbs will generally be shorter.
Osteoarthritis treatment
Treatment of knee joints affected by osteoarthritis requires special scrupulousness and a professional approach. The main forms of treatment are anesthesia complex, a complex of cartilage restorative operations, restoration of other affected parts of the joint, improvement of the motor function of the knee. Simply put, if you start to carry out therapy on time for the treatment of such an ailment, then you can manage to prevent the serious consequences of the disease. If the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee joint of the first or second degree is carried out in time, then it is possible not only to prevent pathological disorders in the joint, but also to participate in the restoration of the destroyed cartilage.
Deforming osteoarthritis is a disease in which joints become inflamed in a non-chronic form. This pathology is based on premature aging and complex wear of the cartilaginous part. All this happens due to the decrease in the main constituents for cartilage, called proteoglycan. How can this manifest itself in reality? In real life, a patient with osteoarthritis has severe pain when moving. If it is arthrosis of the hip joint, the pain will go from top to bottom and significantly radiate to the knee joint. Especially these pains will be felt while walking. To cure osteoartosis of the hip joint, first of all, an anti-inflammatory drug should be used. It is also necessary to use drugs that are able to protect the cartilage, called chondroprotectors. Physiotherapeutic procedures, such as electrophoresis, procedures using current, are also able to reduce pain syndrome.
For the treatment of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint in medical practice, there are several methods. The first method is drug treatment, the second is surgery.
If the patient is being treated with medication, then this procedure will include several stages:
- Complexes of physical education of a therapeutic nature.
- Drug therapy.
In the outpatient treatment of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint, modern drugs are used: medicines that can improve the blood supply to the affected areas of the shoulder joint, a chondroprotector, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, a general muscle relaxant. In the treatment of osteoarthritis of the shoulder, exercise therapy and physiotherapy play a very important role. After all, nothing can compare with the healing massage of the shoulder joint, laser therapy, cryotherapy.
Unfortunately, in medical practice, there are cases when drug treatment has not yielded any results and the patient's condition worsens. Then surgery takes place. There are situations when a person turned to a specialized medical institution very late for help. Then you also have to treat the disease surgically.
In the case of surgical treatment of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint, the patient is inserted a prosthesis instead of the removed joint. Surgical interventions of this level can be partial and complete. With a partial form, only some of the worn parts of the joint change. Complete surgery involves replacing the entire shoulder joint.
Osteoarthritis, in its specificity, can be cured with folk remedies. After all, our great-grandfathers have long used natural resources to the full for the treatment of various ailments.
With osteoarthritis, tumors often occur in the area of diseased joints. This ailment is well cured by compresses, which are prepared on the basis of mustard additives, vegetable oils and honey. The components are mixed in equal proportions, then brought to a boil by smoothly stirring them. This is followed by the ready-made broth thoroughly strain and apply to the sore joints. It is recommended to keep such compresses for about two hours.
It should be noted that the painful effect can be removed by rubbing with a special preparation. Its components include turpentine, castor oil. The proportions should be about 2 to 1. Rub this rubbing into the sore joint once a month.
There are two ways to treat osteoarthritis of the fingers on the hands - operational and medication. It should be noted immediately that the operations are done only in the most extraordinary cases. For example, if medications could not help the patient and the pain sensations undoubtedly increase every day. Then an operation is needed.
First of all, the treatment of osteoarthritis on the fingers should be started with the use of drugs, such as anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs, drugs that restore cartilage, injections consisting of hyaluronic acids to improve the lubrication processes in cartilaginous joints.
Physical therapy, physiotherapy, consisting in such types of treatment as electrophoresis, shock wave therapy, can also help in a qualitative way.
Learn about the diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis