Corrective osteotomy of the humerus. Types of osteotomy: Scarf, chevron, Salter, Akin and others
A knee osteotomy is used when you have early-stage osteoarthritis that has only damaged one side of the knee joint. By shifting weight away from the injured side of the joint, an osteotomy can ease and greatly improve function in your affected knee.
Osteoarthritis can develop when the bones of the knee and lower leg do not line up properly. This can place additional stress on either the inside (medial) or outside (lateral) side of the knee. Over time, this extra pressure can wear away the smooth cartilage that protects the bones, causing pain and friction in the knee.
(Left) Normal knee joint with healthy cartilage. (Right) Osteoarthritis that only damaged one side of the knee joint.
Advantages and disadvantages
Knee osteotomy has three goals:
- Transfer of weight from the affected part of the knee to the healthy area
- To correct knee alignment
- To prolong the life of the knee joint
By preserving its own knee anatomy, a successful osteotomy can delay the need for joint replacement for several years. Another advantage is that there are no restrictions on physical activity after osteotomy - you can comfortably take part in your favorite activities, even active physical exercises.
Osteotomy has disadvantages.
For example, pain is not as predictable after an osteotomy as compared to a partial or total knee replacement. Since you can't put your weight on your legs after an osteotomy, it takes longer to recover than a partial knee replacement.
In some cases, an osteotomy may make late surgical knee replacement more difficult.
Recovery from an osteotomy is generally more difficult than from a partial knee replacement due to the pain and inability to shift body weight to the leg.
Because the results of total knee arthroplasty and partial knee replacement have been so successful, osteotomy of the knee has become much less common. However, it is not a bad option for many patients.
Procedure
In most cases, an osteotomy for an arthritic knee is done on the tibia (tibia) to correct the alignment, which puts a lot of focus on the inside of the knee.

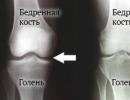
(Left) This x-ray of a healthy knee shows a normal space between the tibia and femur. (Right) In this x-ray, osteoarthritis has damaged the inside of the knee. The tibia and femur rub against each other, causing pain (green arrow).
During this procedure, a wedge of bone is removed from the outside of the lower leg, under the healthy side of the knee. When the surgeon closes the wedge, he straightens the leg. This brings the bones on the healthy side of the knee closer together and creates more space between the bones on the arthritic side. As a result, the knee can bear weight more evenly, which reduces pressure on the affected side.

In a tibial osteotomy, a wedge of bone is removed to straighten the leg.
Tibial osteotomy was first done in Europe in the late 1950s and came to the United States in the 1960s. This procedure is sometimes referred to as a “high tibial osteotomy.”
Femoral osteotomies are performed using the same technique. It is usually done to correct the alignment of the knee.
Candidates for knee osteotomy
Knee osteotomy is most effective for active patients with moderate weight who seek help in the age range of 40 to 60 years. Such candidates have pain on only one side of the knee, and no pain below the kneecap. Knee pain should be caused primarily by activity, and should also remain for a long period of time.
Candidates must be able to fully extend the knee and flex it to at least 90 degrees.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis are not good candidates for osteotomy. Your orthopedic surgeon will help you determine if a knee osteotomy is right for you.
surgical procedure
Before the procedure
You will most likely be admitted to the hospital on the day of the operation.
Before the procedure, a doctor from the anesthesia department will assess your condition. He will review your medical history and should discuss the choice of anesthesia with you. Anesthesia can be either general (you are asleep) or injected into your back (you are awake, but your body is numb below the waist).
surgical procedure
Knee osteotomy surgery usually takes 1 to 2 hours.
Your surgeon will make an incision at the front of the knee, starting below the kneecap. He will plan the correct wedge size using the guide wires. Your surgeon will cut the bone along the guide wires and then remove the bone wedge. It will bring the bones together in order to fill in the space created by removing the wedge. The surgeon must anchor the plate into the bone until the leg heals.
This is the most commonly used osteotomy procedure called wedge closure.
After the wedge bone is removed, the tibia can be held in place with a plate and screws.
In some cases, instead of "closing" the bone, the wedge of the bone is "opened" and a bone graft is added to fill in the space and help correct the misalignment. This procedure is called wedge opening.
After operation
In most cases, patients stay in the hospital for 2 to 4 days after surgery. During this time, you will be monitored and given pain medication.
After surgery, your surgeon may put your knee in brace or cast for protection while the bone heals.
You may need to use crutches for a few weeks.
About 6 weeks after the operation, you should see the surgeon for a return visit. X-rays will be taken so your surgeon can check how well the leg has healed. After an observation, your surgeon will tell you when it is safe to stop using crutches and when you can begin full rehabilitation.
During rehabilitation, a physiotherapist will give you exercises to keep you active and rejuvenate.
You will be able to resume your full activities in 3 to 6 months.
Complications
As with any surgical intervention, there are risks associated with osteotomy. It is up to your surgeon to discuss each of the risks with you and take specific steps to help avoid possible complications.
Although the risks are low and the most common complications include:
- Infection
- blood clots
- Stiffness of the knee joint
- Vascular and nerve injuries
- The futility of osteotomy for healing
In some cases, a second operation may be required, especially if the osteotomy does not heal.
Conclusion
An osteotomy can relieve pain and slow the progression of arthritis in the knee. This may allow the patient to lead a more active lifestyle for many years. Although many patients will eventually require a total knee replacement, an osteotomy can be an effective way to buy time until a replacement is needed.
About the author: Andrey Stepanovich3258 0
Modern medicine has reached a new level, and now surgical operations to eliminate a defect or disease of the bone no longer lead to such dangerous consequences than several decades ago.
One of the most popular procedures today is osteotomy.
This operation can significantly improve the life of a sick person, so specialists perform it without any fear.
What is the essence of the operation?
Osteotomy is a surgical intervention, the purpose of which is to eliminate a defect in the form of bone deformity, as well as to significantly improve the functions of the musculoskeletal system through an artificial fracture.
The operation at first glance looks rather scary, but according to its results, it is much easier for a person to stand if the procedures were carried out on his feet, or to independently perform simple actions and movements with his hands, in case of surgical intervention on the arm.
The operation is carried out in several ways: by incision of the skin or by making holes.
Fastening of broken bones is carried out using plates, screws, knitting needles and other devices.
Plaster bandages are practically not used, since this is fraught with bone displacement and repeated surgical intervention.
Varieties of intervention
As already mentioned above, the operation can be carried out by incision or punctures, as a result of which the osteotomy is divided into open and closed types.
The closed type of intervention is used extremely rarely.
Osteotomy, depending on the intended purpose, is divided into:
- Corrective surgery- It is used due to an incorrectly fused bone after a fracture.
- Derotational operation- is carried out in order to save a person from pathological rotation of the bone.
- Lengthening or shortening of limbs– sometimes has a cosmetic connotation.
- Surgery to improve support function.
Each type has its own characteristics and reasons for holding.
Sometimes bone fractures are cosmetic reasons. For example, in order to carry out a cosmetic surgery to lengthen the legs, osteotomy is used - artificially break bones for their further lengthening.
Corrective surgery
The presented type of osteotomy is used every time when there is a significant deformation of the bones in the human body.
For example, this type of surgical intervention is used in the following cases: 
- improperly fused bone after a fracture;
- the presence of ankylosis of the joint in a vicious position;
- the presence of bone curvature due to rickets and in other situations.
Corrective osteotomy is sometimes performed by lengthening or shortening the bone, if such actions will lead to a positive result and significant relief to the person.
The operation is carried out in three ways:
- Linear with bone graft- the bone is incised in order to align it through the introduction of a bone graft.
- Wedge-shaped with removal of the bone wedge- a part is removed from the bone to align it.
- corner– the bone is cut at an angle on both sides and is set in the correct position due to the necessary correction.
In most cases, corrective osteotomy is used after bone malunion due to a fracture. The operation is performed under general anesthesia and takes a long recovery.
Limb lengthening
Limb lengthening is the most common operation where an oblique osteotomy is used with skeletal traction applied to the distal end.
Such an operation can increase the operated bone by 2-7 cm.
The main condition is the selection of the correct size of the load. The presented method helps not only to "align the curved" bone, but also to significantly increase its length.
When using compression-distraction devices, it is possible to achieve the result of an increase in the length of the bone by almost 20 cm.
This method helps to increase the limb per day by 1 mm, while the mobility and function of the joints are preserved.
Derotational operation
It is often used after dislocations. If the plaster or tight bandage is applied incorrectly, a kind of reversal of the bone relative to the joint occurs.
Such “contact” causes pain and can lead to dysfunction of the joints - a person cannot do simple actions with his hand, in case of damage to the lower extremities, the patient cannot move.
Derotational osteotomy involves cutting the bone in the transverse direction. Next, the central part of the bone is turned in the required direction at a certain angle of turn.
All participating bone fragments are fixed until recovery using a special metal structure. In some cases, suturing of the joint capsule and shortening or lengthening of the tendon is required.
If necessary, after diagnosing an x-ray, the angles of rotation can be adjusted. Recovery after such an operation can take several months.
Support function recovery
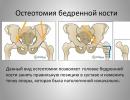
If the patient needs to restore support functions, osteotomy is performed on the hip joints. Here, a place is often created for the support of the hip bone.
The pelvic bones and the thigh itself are subjected to an incision. Such a surgical intervention is performed in the following cases:

Osteotomy for valgus and varus deformity of the lower leg
- the presence of congenital;
- when diagnosing false joints of the femoral neck;
- various deformations - or.
Several methods of bone dissection are also used here, depending on the goal of restoring the support function. The operation is performed exclusively under general anesthesia and requires several months of recovery.
The video clearly shows how a femoral osteotomy is performed:
Features of the operation and its consequences
An osteotomy is the cutting of a bone to improve a person's life.
But such improvements may not be noticed soon, especially since sometimes the operation, although it leads to the elimination of pain during the implementation of simple actions, but from the point of view of the cosmetic aspect, significant defects can be seen.
For example, the joints of the limbs will look asymmetrical, which can cause some discomfort to the operated person.
In addition, immediately after the operation, in most cases, long-term use of crutches (from one to three) months is required.
Despite the patient's uncomfortable position, the patient must take daily walks to restore the function of the operated bone.
The postoperative time is also accompanied by a course of physiotherapy, depending on the nature of the osteotomy. Full recovery can take up to a year.
Osteotomy can lead to certain complications, among which are revealed:
- The beginning of the process of suppuration of the wound- a special role in the presented situations is played by the immunity of the operated patient.
- Fragment Offset- occurs due to poor or incorrect fixation of them, which leads to a second operation.
- Delayed bone healing- based on the individual characteristics of the human body.
- Formed– impaired mobility of the operated bone and joint. A repeat operation is required.
 In connection with the foregoing, it is better to perform osteotomy only after strengthening the immune system, as well as with a professional surgeon who will not allow displacement or suppuration of the wound.
In connection with the foregoing, it is better to perform osteotomy only after strengthening the immune system, as well as with a professional surgeon who will not allow displacement or suppuration of the wound.
The osteotomy has one serious disadvantage. If it is necessary to repeat the operation associated with the replacement of the joint, it will be much more difficult to carry out such an action if the bone has already been dissected.
But in some cases, osteotomy is the only true, possible and reliable solution to eliminate the existing disease.
Bones take on an irregular shape and position if professional help has not been provided after the fracture. The essence of this procedure is that the diseased bone is broken and then fixed with the help of special plates or other devices so that it grows together and takes its natural shape. Osteotomy is used to achieve the following goals:
- return motor functions to the limbs, restore their performance;
- in the practice of plastic surgery, osteotomy is used to lengthen the limbs;
- restore the base function.
Depending on the purpose of the procedure, the object of osteotomy changes. Say, in order to return the support function, this procedure is performed on the hip joint.
Corrective osteotomy is aimed precisely at restoring the position, shape and performance of the limbs after an illness or injury.
The process of the procedure
Training
The process of preparation for this operation consists in an extensive radiograph, during which the orthopedic surgeon receives images of the area that can be corrected from different angles. Thus, he chooses the optimal tactics for conducting the operation.
Corrective osteotomy procedure
Those bone structures that are subject to adjustment are artificially broken by an orthopedic surgeon during the operation, and then fixed at the right angle and in the required position. In order for the bones to grow together correctly, a special plate or other special means, such as knitting needles and bolts, are installed. Thanks to modern technologies and in order to avoid complications in the form of contractures in adjacent joints, gypsum is not applied.
rehabilitation period
Rehabilitation lasts depending on which part of the body was operated on, for example, corrective osteotomy of the knee joint requires 12 weeks of rehabilitation. Moreover, the bones grow together for the first two months, the rest of the time they acquire the necessary strength. During this period of time, loads on the operated part of the body are excluded.
Indications
Corrective osteotomy is indicated for malunion of fractures. In addition, diseases such as:
- different types of arthrosis, including osteoarthritis and gonarthrosis;
- ankylosis of bones;
- rickets.
In addition, this operation is performed to delay the need to replace the joint with an artificial one, as well as to correct the prosthesis.
Contraindications
Osteotomy is contraindicated in diseases of the kidneys and liver, in disorders of the cardiovascular system. It can not be carried out if the patient has an exacerbation of any chronic disease, as well as in acute diseases. It is impossible to do an osteotomy for those who suffer from any diseases of a purulent nature.
Complications
This surgical operation is complex and quite risky. The following complications may occur:
- slow fusion of bones;
- the formation of suppuration;
- incorrect change in the position of the wreckage;
- the appearance of a false joint.
Prices and clinics
This operation is carried out only in well-equipped medical centers. For its implementation, specific experience of the doctor is required. Prices for corrective osteotomy depend on the nature and complexity of the operation.
The main idea of the operation is forced deformation (breaking) of bones and subsequent correction of hard tissues. Its purpose is to correct an incorrectly fused fracture. The type of osteotomy is determined by specialists and depends on the location and complexity of the problem.
Operation goals
The effectiveness of the procedure is confirmed by positive statistics. Often osteotomy of the knee joint is used to cure such a serious disease as deforming arthrosis. Manipulation successfully copes with pathology and helps to postpone the installation of implants for a long time up to a decade, and sometimes even longer.
Osteotomy is an artificial bone fracture and subsequent competent fusion, which:
- eliminates deformations;
- relieves pain;
- gives patients the opportunity to lead an active lifestyle and play sports.
Corrective surgery is applied to all bones:
- tibial;
- hips;
- feet;
- phalanges of fingers.
Procedure Types
The most popular options are:
- Osteotomy of the tibia. Its essence is the elimination of the wedge-shaped area below the knee joint. Straightens the axis of the legs, removes pain.
- Osteotomy of the femur. It is done on the area above the knee. Normalizes the functioning of the joints, treats lameness.
Advantages and disadvantages

Designed for people under 60 years old. Advantages of the operation:
- a positive result for the state of the knees and adjacent ligaments;
- delay of full arthroplasty for 5-10 years;
- further normal life without limitation.
Corrective osteotomy of the knee joint has disadvantages:
- longer rehabilitation;
- possible severe complications;
- the use of artificial structures for fixation;
- auxiliary unreliable factors.
Indications for carrying out
Osteotomy is also indicated for:
- arthrosis;
- unsuccessful splicing after fractures;
- congenital curvature;
- diseases affecting the curvature of the legs;
- ligament stretching.
Main stages
Doctors conduct a thorough diagnosis and prescribe additional tests to prevent:
- amplification of the pain syndrome;
- further deformation.
Corrective osteotomy of the tibia is performed by a surgeon or orthopedist.
Preparatory stage

It is an in-depth diagnosis, during which the specialist analyzes:
- the patient's health status;
- the degree of deformation of the articular tissues.
Usually assigned:
- digital x-ray;
- CT. A very effective method that demonstrates even minor bone defects.
Having collected the necessary data, the orthopedist and surgeon:
- make a prognosis for the operation;
- draw conclusions about the distortion of the axes;
- study the ratio of reference angles.
The doctor conducts a consultation with the patient, at which he talks about:
- possible negative consequences;
- stages of osteotomy.
Also, at the preparatory stage, the type of procedure is determined, which depends on:
- distance to the joint;
- the design used for fixation;
- degree of deformation.
The patient, for his part, stops taking the drugs agreed with the doctor within 7 days.
Operational stage

Each version of the procedure has slightly different technical characteristics. But the basic execution scenario is similar for all types:
- The knee is excised, the edges of the incision are moved apart by a pre-calculated step.
- An artificial part or fragment of the pelvic bone is placed inside. Its volume is determined using special software.
- Metal plates are superimposed on top for fixation. Carving helps to improve the future result. Pillars and spokes contribute to the achievement of even greater strength of the structure. Competent execution of this stage ensures the correct angle during movements.
- The whole procedure is carried out under constant supervision with the help of an X-ray, which catches any shortcomings and controls the progress of the surgical intervention.
If everything is done correctly, then:
- the patella and tendons remain intact;
- local blood flow is improved;
- cartilage is slightly corrected;
- the pain syndrome disappears.
Postoperative stage
Several factors influence the duration and success of rehabilitation:
- patient health;
- regenerative capabilities of the musculoskeletal system;
- the quality of the connectors.
Lasts from 3 to 12 months.

During the first 60 days, the bones quickly grow together, connective tissue builds up. In the remaining period, the strength and reliability of the new structure increases. Doctors advise in the first days to give some load on the operated leg. Limbs are mastered with a new joint after six months.
Osteotomy is one of the simple and modern methods that keep the legs healthy. It is recommended for young people who want to return to their normal lifestyle as soon as possible, which includes physical activity and training.
Alternatives
To achieve a long-term result and effectively eliminate pain, the doctor may recommend:
- Partial knee replacement (unicondylar knee arthroplasty). Healthy parts of the joint are not touched, only the sick ones are replaced.
- Partial or total joint replacement.
Contraindications and possible complications
Osteotomy has a number of contraindications:
- acute stage of rheumatoid arthritis;
- patellofemoral arthrosis at stage 3;
- arthrosis that has spread to the collateral part of the joint;
- osteoporosis;
- excess weight;
- infections in the bone tissue;
- reduced regeneration.

Since any operation carries a certain risk to health, it is the doctor's duty to tell the patient about the possible complications that he may face after osteotomy. Such scenarios include:
- Wound infection. Taking antibiotics may help.
- Offsets. They are corrected by reposition and fixation in the correct position.
- Insufficient healing rate. In this case, the intake of multivitamins focused on calcium and other trace elements necessary for the construction of new bone tissue is additionally indicated.
- False joint. Fixed with a new operation.
- Reduced sensitivity at the site of the procedure. Over time, it goes away on its own, does not need treatment.
- When replacing some parts with artificial ones, the human body may begin to reject foreign objects. Helps endoprosthesis.
Osteotomy is a high-tech procedure that helps to get rid of the deformation of the axes of the lower extremities. Recommended primarily for young people leading an active lifestyle. Before carrying out, the specialist takes into account the possible consequences and contraindications and then determines the options for surgical intervention.
Corrective osteotomy of the knee joint is a proven method of surgical treatment of deformities of the tibia and femur. This operation reduces the load on the articular surfaces, eliminates existing pathologies and slows down the degeneration of the lower limb.
Schematic representation of the operation.
What is a knee osteotomy?
Corrective osteotomy of the knee joint is an operation that eliminates congenital and acquired bone deformities. During surgery, the doctor cuts out a predetermined area of bone tissue and connects the free bone fragments with implants. As a result, the axis of mechanical load is transferred to a healthy part of the joint. The operation is performed under general or spinal anesthesia. After treatment, the orthopedist fixes the lower limb of the patient with a plaster cast for the recovery period. Rehabilitation is underway.

The described method of correction is traditionally compared with knee arthroplasty. Osteotomy is a less traumatic treatment. This medical manipulation is great for young patients suffering from advanced stages of gonarthrosis. The choice of osteotomy as a method for restoring the mobility of the lower limb makes it possible to postpone arthroplasty for a long time.
Osteotomy has been used for two centuries. After the discovery of methods of replacement arthroplasty, this surgical intervention faded into the background, but this method of treatment is still used. At the beginning of the 21st century, modern methods of fixing bone areas were developed, which reduce the duration of rehabilitation.
Indications for surgery
The main indication for surgical intervention is gonarthrosis. This is a degenerative disease of the knee joint, which is manifested by the gradual destruction of cartilage and deformity of the lower limb. In the later stages of gonarthrosis, patients develop valgus and varus deformities. The range of motion is limited, there is a chronic pain syndrome.

Other indications:
- Congenital deformity of the lower limb.
- Bone curvature after trauma.
- Preparation for knee arthroplasty.
- Displacement of the axis of the lower limb in pathologies of the articular ligaments.
- Rickets, osteitis deformans and other bone diseases.
The intervention is recommended for a satisfactory condition of the cartilaginous surface of the bones and an isolated lesion of one area of the knee joint. This method of correction makes it possible to preserve the mobility of the lower limb in young patients.
When will an osteotomy not help?
The effectiveness of treatment depends on the age, sex and body weight of the patient. Unsatisfactory results of the operation may be due to the patient's advanced age, significant bone damage and destruction of hyaline cartilage.
Conditions in which intervention is inappropriate:
- osteoporosis;
- extra-articular pathologies;
- lack of blood supply to the lower limb;
- violation of bone growth;
- absence of a meniscus;
- severe obesity (BMI: 40 and above).
If the indications are not properly assessed, osteotomy can accelerate the degeneration of the knee joint. Before treatment, doctors conduct laboratory tests, take pictures of the lower limb throughout and prescribe additional diagnostic manipulations.
Types of surgical techniques
Interventions are classified according to the place of execution, the method of tissue excision and the nature of bone grafting. The structure of the tibia or femur is corrected. Classification according to the nature of the repair includes open, closed, lateral and direct osteotomies. Tibia correction can be high or low. The specific surgical technique is selected by the doctor individually based on the results of a preliminary examination.
The main types of osteotomy:
- Wedge closed. A skin incision is made in the lateral or anterior region of the knee to access the superior tibial epiphysis or inferior femoral epiphysis. After excision of the tissue, the free surfaces of the bone are fixed with metal plates or staples.
- Wedge-shaped open. After a skin incision in the anterior or lateral region of the knee, an incomplete osteotomy is performed. The end section of the tibia is separated into two parts with the formation of diastasis. Next, the bone sections are connected with a metal plate and an autograft from the patient's pelvis.

Osteotomy of the knee joint: a visual representation of the procedure.
Bone tissue is removed using an osteotome. To prevent damage to the vessels and nerves passing through the knee joint, the correction is carried out under the control of a fluoroscope or X-ray machine. After plastic surgery, the skin is sutured, and the lower limb is fixed with a plaster cast or splint.
There is no single method of surgical intervention suitable for all indications. When choosing a surgical technique, the doctor takes into account the planned angle of correction. Imaging techniques help to more accurately restore the axis of the lower limb. In modern orthopedics, an open wedge osteotomy of the tibia above the level of tuberosity is most often performed.
Rehabilitation
The results of treatment in the long term depend on rehabilitation measures. After surgery, the doctor conducts control examinations and selects methods for restoring the mobility of the knee joint. The goals of rehabilitation include the elimination of pain, the prevention of postoperative complications and the restoration of the muscular apparatus of the lower limb.
Rehabilitation methods:
- Physiotherapy: electrical stimulation, cryotherapy and thermal effects. Physical therapy relieves pain and reduces tissue swelling in the postoperative period.
- Massotherapy. Manual therapy improves blood flow in tissues, relieves pain and normalizes muscle tone.
- Physiotherapy . Exercises can be done at home. The main task is to restore flexion and extension movements in the knee joint.
- Orthopedic rehabilitation to prevent recurrence of the disease. The patient is advised to wear a knee brace or an elastic bandage to fix the joint. For the first time after the operation, it is necessary to use a cane and wear shoes with orthopedic insoles to reduce the load on the articular surfaces.
The rehabilitation scheme is drawn up by an orthopedist and an exercise therapy doctor. Selected drug therapy. Full recovery of motor activity occurs within a year.
Life after treatment
The prognosis is determined by the initial diagnosis, the chosen technique of surgical treatment, the qualifications of the surgeon, the age of the patient, and other criteria. According to the G. A. Ilizarov Medical Center, positive results were noted in 95% of patients after the intervention. Within 10 years after bone grafting, there is no pain and other symptoms of gonarthrosis. Young people who have undergone osteotomy, after rehabilitation, return to a full life. Subsequent replacement arthroplasty is facilitated.
The long-term results of the correction are difficult to predict. Patients are advised to visit the orthopedist regularly and undergo examinations to monitor the condition of the joint. Osteotomy as an independent method of treatment does not completely eliminate arthrosis, but only slows down the development of degenerative processes. In some patients, relapse occurs as early as 4 years after the intervention.
Prices for knee osteotomy
The cost of treatment depends on the qualifications of the doctor, surgical technique and diagnosis.
Average prices:
- Moscow: from 7 to 22 thousand rubles.
- St. Petersburg: from 10 to 23 thousand rubles.
- The average price in Russia is 15 thousand rubles.
Information on prices must be clarified in a particular clinic.