What research sees a polyp in the uterus. What complications can arise after surgical removal of uterine polyps? Alternative treatment of polyps.
Nature assigned the main task to the female sex - the bearing and birth of healthy children. However, various gynecological diseases worsen the state of reproductive function. In advanced form, infertility develops, benign and malignant tumors, including polyps in the uterus, the causes of which are diverse.
To date, there is no unified theory regarding how polyps occur. Until now, gynecologists have not come to an agreement, despite the development of diagnostic technologies and medicine itself.
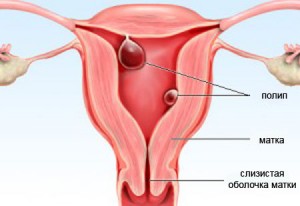
Polyps are benign lesions that affect the mucous lining of the uterine cavity - the endometrium and have a branching structure. Their size can vary from a few centimeters to the size of an average apple.
The causes of the disease
- Insufficient exfoliation of the endometrium. Normally, the mucosa before the onset of the menstrual period is separated and then washed naturally. The formation of neoplasms begins when the lining does not completely depart. When polyps grow to a certain size, they are fixed on the growing mucosa with a thin leg. the reasons for the formation (formation) of which lie in the insufficient exfoliation of the endometrium, are treated on average from three to six months.
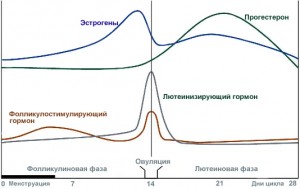
- Spontaneous education. In this case, the cause are violations and malfunctions of the hormonal background. An increase in estrogen levels occurs after the use of oral contraceptives, hormone replacement therapy, and pregnancy. Uneven production of sex hormones leads to serious imbalance. Against the background of a sharp increase in estrogen levels, gestagen drops to a critical level. This provokes negative changes in the direction of changes in the mucous membrane of the genital organ. Polyps in the uterus, the causes of which are caused by hormonal imbalances, are treated with a course of special therapy.
- Inflammations specific and nonspecific in acute or chronic form. One of the reasons for the development of serious painful processes can be postponed abortion. As a rule, the doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics after surgery, but with unsuccessful therapy, inflammation still develops, and the formation of polyps is almost inevitable. It also includes colpitis, adnexitis, cervicitis, vaginitis, bacterial vaginosis.
- Infectious lesions transmitted by sexual intercourse.
- Endocrinological pathology. Risk factors include diseases such as diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, and obesity.
- Unsuccessful pregnancy, history of placenta after childbirth.
- Injuries. Very often it is the body or neck, perineum.
- Unprofessional gynecological manipulations.
- Intrauterine device It can be dangerous to wear them for a long time.
- Hereditary and genetic predisposition.
- Anomalies, pathologies of the development and location of the organs of the female reproductive system.
- Pathological proliferation of medium and small vessels inside the uterus. Around the tissues, epithelial cells begin to form.
- Endometriosis, fibromyoma, dysplasia, cervical erosion.
- Hypodynamia, which provokes the occurrence of stagnation in the pelvic organs and hypoxic phenomena localized in the appendages.
- Age group from forty to fifty years. Polyps in the uterus, the reasons for the formation and development of which lie in age-related changes, are most often removed with the help of surgical intervention.
Diagnostic Features
Uterine polyps are often detected during a routine examination by a gynecologist. The doctor, manipulating a special mirror, sees them on the mucous membrane. For a more accurate diagnosis, colposcopy, an additional x-ray examination, gitseroscopy, which allows you to thoroughly examine the uterine cavity, are performed. A reliable picture of the disease helps to determine and ultrasound.
Polyp classification
Pathology is classified by the number of polyps and their histological structure. Formations can be multiple or single. By structure, polyps are divided into:
- Glandular uterine polyps. Formations develop due to violations in the endometrium.
- The most common type of pathology. The size of the formation can reach several centimeters, it has a tendency to degenerate into a malignant tumor. Adenomatous polyps in the uterus, the causes of which can be any, according to gynecologists are considered the most dangerous.
- Fibrous polyp. It is very dense in its consistency because it is formed by fibrous tissue. It is perfectly visualized with ultrasound.
- Mixed, or glandular fibrous.

Symptomatology
Every woman should undergo a regular gynecological examination (at least once a year). This is especially true if there is at least one risk factor for the development of the disease. You should carefully listen to the state of your body, since polyposis manifests itself as follows:
- Inability to conceive.
- Violations, cycle failures, in particular, towards polymenorrhea. During this period, abnormally heavy bleeding occurs.
- Irregular ovulation.
- Excessive uterine bleeding or discharge (spotting with bloody stains).
- Dyspareunia - soreness during sexual intercourse.
- Discomfort in the abdomen, pulling, gripping pains.
- In rare cases, general intoxication symptoms.
Prevention
As you know, to prevent any disease should be prevented. So, a woman should from time to time undergo examination by a gynecologist, adhere to diet food, and also exclude irritating factors (overheating, hypothermia, etc.).
A good prevention is the lack of promiscuous sexual intercourse, regular sexual activity, the use of contraceptives (hormonal) exclusively if necessary and as directed by a doctor, an active lifestyle. Only then is it likely that a woman will never have polyps in the uterus. The causes and various treatment methods have been studied in detail, but there is always a risk of developing negative consequences.

Modern treatment methods
The earlier a disease is diagnosed, the easier it is to get rid of it, and the less harm it will cause to the body. A small formation can be cured by taking a course of anti-inflammatory or hormonal therapy. If the situation has gone too far, then the polyps are removed surgically.
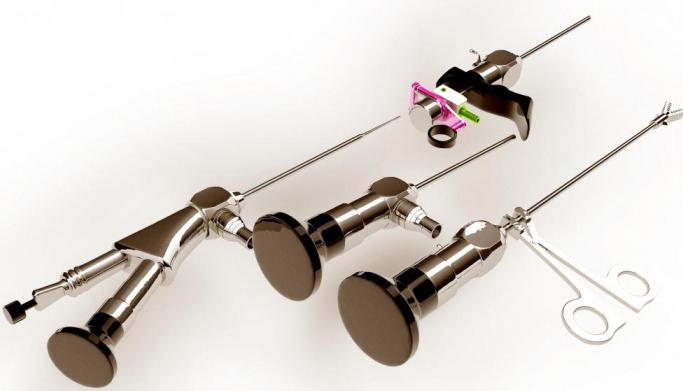
Modern techniques are less traumatic and effective. Polyp removal can be done using hysteroscopy. A special tube is inserted into the uterus, at the end of which there is a micro-video camera. Tweezers are fed through a special channel, through which the formation is excised, in some cases, instead of tweezers, a loop is used that captures the polyp around the leg. This leads to the separation of education from the uterus. After removal, the place where the tumor was located is cauterized with liquid nitrogen.
When a large accumulation of tumors is diagnosed or their size is too large, an additional curettage procedure is performed. This ensures the complete destruction of such an formation as a uterine polyp. The causes and consequences of surgical intervention are studied in detail in modern medicine. The risk of relapse remains minimal.

Treatment without surgery
If the patient refuses surgical intervention, and when polyps in the uterus are the result of hormonal imbalance, the doctor can use conservative treatment with the help of various groups of medications:
- COCs - combined oral contraceptives. With their help, therapy of focal endometriotic hyperplasia is carried out. The technique is used mainly in women of the reproductive group, whose age does not exceed 35 years, or in the teenage period. High efficiency is achieved during diagnosis. In some cases, the use of contraceptives avoids curettage in girls with polyps suffering from uterine bleeding. Several tablets are prescribed at once, after which the dosage is gradually reduced.
- Gestagens. Preparations with progesterone are taken mainly in the second phase of the cycle. Treatment can last up to six months. The activity of the endocrine system is normalized and the hemostatic effect is realized.
- Releasing hormone agonists. Treatment is prescribed to women who have reached 35 years of age, while eliminating the total course of therapy is quite long - up to six months.
- Antibacterial therapy for the treatment of infectious and inflammatory lesions.
- Multivitamin complexes.
Polyps in the uterus, the symptoms and causes of which are established and are under qualified control, are successfully treated. Regardless of the etiology of the disease, a favorable prognosis is 85%.

Relapses
When diagnosing repeated formations, there is a risk of degeneration of a benign polyp into a malignant one. The percentage of probability of such a development of events is low, however, gynecologists recommend taking treatment and hormonal therapy seriously. The main risk factor is adenomatous polyps. After the treatment, the woman is registered with a gynecologist until the cycle normalizes.
Effects
In the postmenopausal period, polyposis often provokes the formation of a malignant tumor. For women of reproductive air, the consequences of this disease can also be no less sad. So, polyposis can provoke the occurrence of prolonged hormonal failure and infertility.
Polyps in the uterus symptoms, causes and treatment: conclusion
Over the past decades, women of reproductive age and menopause, who are at risk of polyposis, have often come to see doctors. The causes of the development of the disease are different, with large quantity variations, which leads to the growth of patients who are diagnosed with polyps in the uterus. What causes them? What symptoms are characteristic? All information was presented above. In any case, it is necessary to understand that the danger lies in the degeneration of the polyp into a malignant formation, therefore it is so important to diagnose the disease in time and start treating it at an early stage.
Many diseases of the uterus are caused by processes of hyperplasia. Uterine polypnot an exception, as it is formed due to the growth of the endometrium, is located on a leg or a thick base. Such neoplasms can cause bleeding from the genital tract, periodic pain, worse during sexual intercourse, and infertility.
Typically, polyps do not extend beyond the uterus, however, cases of their germination through the cervix and damage to the mucous membrane of the external genitalia of a woman are sometimes recorded. Cancer data are detected at reproductive age and menopause. The frequency reaches 15-20% among the entire gynecological pathology.
What are uterine polyps?
Benign formations that form on the uterine mucosa and rise above its surface are polyps in the uterus. Their sizes can vary from 3-4 millimeters to 5 centimeters. Found on a stalk or wide base, located singly or in clusters.
With multiple lesions, one should speak of polyposis.
Why are polyps formed in the uterus?
The formation of such oncological formations on the mucosa may be due to:
- hormonal imbalance, in which there is an increased level of estrogen, due to which polypous growths begin and appear. In addition, a woman can be diagnosed with glandular endometrial hyperplasia, and polycystic ovaries;
- inflammatory processes (endometritis, cervicitis, adnexitis);
- long-term ongoing sexual infections;
- mucosal trauma due to abortion, diagnostic curettage or prolonged standing of the IUD (spiral);
- endocrine pathology (thyrotoxicosis, diabetes, obesity);
- immune dysfunction.
Also, it is necessary to add a change in the psycho-emotional state when a woman is disturbed by frequent stressful situations.
Symptoms
Symptomatically suspecting the appearance of a polyp in the uterus is almost impossible, since at the initial stage there are no clinical signs. As soon as a polypous formation reaches a certain size, a woman begins to worry about spotting from the genital tract.
They are observed in the intermenstrual period, before menstruation, after sexual intercourse and in the menopause. As a result of the constant release of blood, anemia increases, weakness, dizziness and pallor of the skin appear.
If it reaches a large size, an additional appearance is possible:
- mucous discharge;
- pain in the lower abdomen cramping in nature;
- discomfort and pain during intercourse;
- infertility.
As for pregnant women, they significantly increase the risk of spontaneous abortion and premature birth.
Manifestation
Polypous cancer formations can necrotic due to insufficient intake of nutrients and oxygen. Also, upon penetration infectious agent inflammation of an infectious origin develops.
Based on the morphological structure, there are:
- glandular type (found in adulthood);
- fibrous (characteristic for the age over 40);
- mixed;
- adenomatous - has signs of proliferation, glandular remodeling, which predisposes the cancer process.
Separately, it should be said about the placental form, which is formed due to incomplete removal of the placenta during a frozen pregnancy, after childbirth or a miscarriage.
Regardless of the structure, with the appearance of spotting that is not associated with the menstrual cycle, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Can a uterine polyp go into cancer?
Polypous growth is considered, therefore, its mandatory removal and histological examination is necessary. Depending on the area affected by polyps, removal of the neoplasm can be performed with hysteroscopy or diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity. In addition, if necessary, hysterectomy can be performed (organ removal).
Uterine Polyp may recur, that is, reappear. In 1.5% of such cases, their malignancy is noted, especially due to the adenomatous type. In this regard, after the removal of education, further observation by an oncologist is required.
Factors in which a uterine polyp can go into cancer
Among the factors that can provoke a malignant transformation of polypous formations, it is worth highlighting:
- decreased immune defense of the body;
- infection of the body, including sexual infections;
- exacerbation of the inflammatory process in the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes;
- overheating in the sun, in the sauna;
- hormonal surge due to stressful situations or activation of concomitant endocrine pathology.
Most common cause malignancy of a polypous neoplasm is its trauma. This can occur during diagnostic curettage, abortion and other gynecological manipulations.
How to recognize cancer transformation?
The malignant process is not always able to be detected at an early stage, based on the symptoms. Diagnosis in this case consists in the study of smears, identification of tumor markers in the blood and histological analysis of the material removed during diagnostic curettage.
Symptomatically, cancer can be suspected as the process progresses, when a woman begins to be bothered by fetid discharge, bleeding, and ultrasound reveals heterogeneity of the uterine tissues, its increase and the presence of an additional formation with fuzzy contours.
Cancer Prevention
To prevent malignancy of polyps, it is recommended to avoid stressful situations, not to overheat under the sun, in a sauna, to monitor the activity of chronic infections and inflammatory processes. Moreover, uterine polyp must be removed in a timely manner, which will significantly reduce the risk of tissue malignancy.
- Medical indications
- Why does the disease occur?
- The course and diagnosis of the disease
- Neoplasms in expectant mothers
- Therapies
- Other therapies
- Unconventional recipes
- The use of a golden mustache, onion
- Additional unconventional recipes
- Prevention of ailment
With polyps in the uterus, symptoms and treatment depend on their location. A benign neoplasm of a mushroom-like form in itself does not pose a threat to the life of patients. But the disease is attributed to precancerous conditions, since in the absence of treatment it degenerates into a malignant neoplasm. Is it possible to get pregnant with a polyp in the uterus? This question interests many women. 
Medical indications
Outgrowths occur on the mucous membranes, so they are detected on the inner surface of the uterus (endometrium) and its neck. Often, an endometrial polyp occurs in women before menopause (after 40 years).
Doctors distinguish specific signs, the appearance of which indicates an endometrial polyp:
- menstrual irregularities (irregular, painful periods);
- heavy bleeding during menstruation;
- bloody, contact bleeding after sexual intercourse;
- soreness in the lower abdomen;
- infertility.
Often a polypous disease in the cervix is \u200b\u200basymptomatic. An illness is detected by chance, during preventive visits to a gynecologist, with an ultrasound of the genitourinary organs. What is a polyp? These are small round nodules (up to 1 cm in diameter). There are single or multiple growths with burgundy, purple, yellowish color. Their surface is porous. Due to its thin shell, the uterine polyp is visualized with a large number of vessels.
Back to the table of contents
Why does the disease occur?
The causes of the formation of the disease have not been studied. Presumably, the etiology of the disease is abortion, hormonal imbalance, cervicitis and other factors. Signs of the disease arise due to the high content of female hormones (estrogens) in the blood. This causes the growth of the inner layer of the uterus, causing the appearance of polyps or endometrial hyperplasia.
In addition, progesterone deficiency leads to the active growth of tumors. Polyp during pregnancy is provoked by vascular growths. Vessels can clog, grow. Epithelial cells located around neoplasms are intensively divided.
The inflammatory process involves the accumulation of immune cells in the tissues of an organ. They are designed to destroy the infection. But at the same time they stimulate the growth of the endometrium. Abortions and unsuccessful curettage provoke the development of erosion, enhancing cell growth in some areas of the uterine mucosa.
The glands in the female body are interconnected. The pathology of some (the thyroid gland, liver, adrenal glands) causes a malfunction in the ovaries and overproduction of sex hormones. This can lead to the formation of polyps in the uterus.
Other causes of the disease:

Back to the table of contents
The course and diagnosis of the disease
Manifestation of the disease: ovarian function is initially impaired. This triggers a surge a large number estrogen into the blood. In this case, the endometrium grows, local growths appear. Then they sprout with vessels and connective fibers, turning into polyps.
To identify polyps of the cervix, the diagnosis is complex. Ultrasound is initially performed. This is the most affordable, painless, safe way to research. The most accurate results are shown by intravaginal examination. Polyp of the cervix during pregnancy is diagnosed only by ultrasound using an external sensor.
If necessary, hysteroscopy is performed. Thin tubes with a camera are inserted into the uterine cavity. With their help, they inspect the organ cavity, examine the mucous membrane. The method allows you to take tissue particles from different parts of the body (for further study). If necessary, a special contrast is introduced into the uterus for further x-ray examination.
Back to the table of contents
Principles of neoplasm classification
 Polyps are attached to the organ wall due to narrow and short legs. If they are long, polyps hang in the vagina. There are several subspecies of the considered neoplasms. By location:
Polyps are attached to the organ wall due to narrow and short legs. If they are long, polyps hang in the vagina. There are several subspecies of the considered neoplasms. By location:
- Cervical polyps are neoplasms attached to the cervical canal with a short leg.
- Polyps of the uterine body - they are often detected on the inner surface of the organ, in its upper part. They have the form of a nodule.
According to the cellular composition, polyps are:
- Glandular - often develop at a young and young age. Remind cysts filled with fluid. Often occur with endometrial hyperplasia.
- Fibrous polyps consisting of connective tissue cells. They are distinguished by their density. They usually develop after forty, more often before menopause and during menopause. The appearance is associated with hormonal imbalance.
- Glandular fibrous masses - consist of uterine cells and connective tissue.
- Adenomatous growths or polyps-adenomas. Consist of mutated, atypical cells. Their signs indicate a precancerous condition.
- Placental growths - arise from particles of the placenta remaining after childbirth.
Back to the table of contents
Neoplasms in expectant mothers
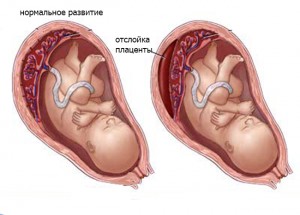 It has been proven that women with polyps can become pregnant, endure and give birth to a healthy baby. But such an ailment causes many complications. Often, growths provoke detachment of the placenta, due to which the child does not receive oxygen and nutrition. At the same time, development is delayed, increasing fetal hypoxia. There is a risk of miscarriage. Any trauma to the growth causes a bloody or blood flow, which negatively affects the child.
It has been proven that women with polyps can become pregnant, endure and give birth to a healthy baby. But such an ailment causes many complications. Often, growths provoke detachment of the placenta, due to which the child does not receive oxygen and nutrition. At the same time, development is delayed, increasing fetal hypoxia. There is a risk of miscarriage. Any trauma to the growth causes a bloody or blood flow, which negatively affects the child.
Treatment of uterine polyps and pregnancy are incompatible. Throughout pregnancy, it is important to maximize the baby's condition.
During pregnancy, there is an independent resorption of polyps (estrogen levels fall, so there are no prerequisites for further growth of polyps).
A modern and reliable way to cure an ailment is surgical intervention. To combat a single polyp, its excision is used, and multiple small growths are scraped out together with the upper layer of the mucosa.
The decision on surgery is made by the attending physician if:
- conservative therapy with hormonal drugs is ineffective;
- the patient's age exceeds 40 years;
- the size of the neoplasm exceeds 1 cm in diameter;
- atypical cells capable of developing into malignant neoplasms were found in the growth.
Back to the table of contents
Therapies
 With polyps in the uterus, symptoms, treatment are interrelated. Removal of polyps (polypectomy) is a gentle and bloodless procedure. Hysteroscopy is a less traumatic procedure used to clarify the localization of a neoplasm and its subsequent removal. Manipulation is performed under "light" anesthesia (regional or general) and lasts up to 20 minutes.
With polyps in the uterus, symptoms, treatment are interrelated. Removal of polyps (polypectomy) is a gentle and bloodless procedure. Hysteroscopy is a less traumatic procedure used to clarify the localization of a neoplasm and its subsequent removal. Manipulation is performed under "light" anesthesia (regional or general) and lasts up to 20 minutes.
The operation is performed on the 2nd day of a new menstrual cycle. The tumor "under the root" is removed. A single growth is removed with forceps, twisting together with the vessels that feed it. The bed of growth is scraped out by a curette, treated with an antiseptic. The recovered tissue is examined in laboratories. The method minimizes the risk of relapse of the disease.
The operation has the following advantages:
- security;
- painlessness;
- quality control of the operation;
- lack of incisions and postoperative sutures.
Back to the table of contents
Other therapies
Laparoscopic treatment is performed through micro-incisions in the lower abdomen. With their help, a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) is performed if atypical cells are detected in the polyps. A laparoscope with a camera allows you to examine the state of the organ, excise it and remove it from the abdominal cavity. The operation has the following advantages:
- painless;
- does not cause complications;
- leaves no scars;
- after the procedure, the body is quickly restored.
 Perhaps non-surgical treatment of uterine polyps. With this method, you can overcome a single small polyp. Using this technique, it will decrease or completely disappear. A similar treatment is used in girls and adolescents, since surgery can lead to infertility.
Perhaps non-surgical treatment of uterine polyps. With this method, you can overcome a single small polyp. Using this technique, it will decrease or completely disappear. A similar treatment is used in girls and adolescents, since surgery can lead to infertility.
Use hormonal medications that reduce estrogen levels, but increase the concentration of progesterone. They are able to eliminate the cause of the disease, quickly eliminating polyps. Patients under 35 years of age are prescribed:
- Jeanine;
- Regulon;
- Yarina.
The course of therapy - at least six months according to a special scheme prescribed by the attending physician. Older patients use gestagens:
- Dufaston;
- Norkolut;
- Utrozhestan.
Drug therapy lasts up to 1 year. Such medications help protect the body from the harmful effects of sex hormones. These are the drugs of choice for menopausal disorders. All patients, regardless of age, are prescribed antibiotic therapy (if there is inflammation). You can get rid of polyps in the uterus by Zitrolide, Monomycin. After treatment, patients should be monitored by a specialist, undergo periodic medical examinations.
Since neoplasms in the uterus are benign in nature, they are not life threatening. However, sometimes they turn into malignant tumors. Polyps in the uterus, the symptoms and treatment of which can only be determined by a gynecologist, are found in women of different ages. Regardless of whether the neoplasms cause discomfort or not, experts recommend removing them surgically or using conservative drug therapy.
What are polyps in the uterus
This is a benign formation that occurs in the uterine cavity, as a result of the growth of the endometrial mucosa (organ membrane). The polyp often has the appearance of a small process, however, it can reach 2-3 centimeters. In the female body, 2 types of formations can develop: a polyp of the cervix and its body. As a rule, at an early stage of development, such growths are treated at home, but with a late diagnosis of pathology, surgery can not be dispensed with.
A polyp of the body of the uterus or cervix of a female organ can occur in a single amount or in groups of several entities. They look like yellowish or dark violet small cylinders with a porous structure. Blood vessels are visible through their thin membrane. Gynecology divides the polyps in the uterus into three varieties that have characteristic differences. These include:
- Fibrous. Appear as a result of hyperplasia (proliferation) of the connective tissues of the organ. As a rule, they develop in parallel with another type of neoplasm.
- Glandular. More common in young than mature women. They grow from the gland tissue.
- Adenomatous. The formation of polyps is accompanied by the formation of adenomas. This species is considered the most dangerous, since adenomatous growths often stop in malignant tumors.
Symptoms
During menopause, any spotting, regardless of their quantity and frequency, is an alarming bell, because they can talk about the development of uterine oncology or hyperplasia. If a similar symptom is observed in a woman older than 40-50 years, who for a long time did not have a period, it is worth immediately visiting the gynecologist's office. Signs of uterine polyps are:
- pain in the lower abdomen (with large polyps);
- irregular periods;
- whitish discharge between menstruation;
- infertility;
- spotting during the absence of menstruation;
- severe bleeding during menstruation.

Reasons for education
One of the common causes of polyposis is hormonal failure in the female body. Less commonly, neoplasms result from chronic genital infections. As a rule, polyps in the cervix, the symptoms and treatment of which are individual, are diagnosed in women from 40 years old, but pathology can also develop in young girls. More rare causes of the disease are:
- transferred injuries of the uterine neck (polyps in the uterus after curettage, abortion, prolonged wearing of the spiral);
- endocrine system diseases (obesity, diabetes, thyroid pathology, hypertension);
- suppressed immunity;
- severe depression and stress;
- incomplete removal of the placenta after an aborted pregnancy;
- inflammation of the appendages, infections in the genitals.

What is dangerous polyp in the uterus
The endometrial polyp, according to doctors, is a precancerous condition. A dangerous consequence of such neoplasms is their transformation into a malignant tumor. In addition, polyposis can cause infertility or a malfunction of the menstrual cycle, which subsequently stimulates the development of anemia (its symptoms are weakness, fainting, tiredness). Polyp during pregnancy often complicates the period of gestation and childbirth. Neoplasms deform the membrane of the female organs, which reduces the chances of a normal fastening of the fertilized egg.

Uterine polyp removal and hysteroscopy
To diagnose uterine polyposis, doctors do an ultrasound scan, metrography, and hysteroscopy. Using these procedures, a specialist determines the state of education, its size and location. If the growths are accompanied by inflammation, so that the polyps disappear, it is only necessary to remove the focus of infection. With a hysteroscope, a gynecologist can remove even large tumors, minimizing the risk of complications.
As a rule, treatment of the uterus for polyposis is carried out through surgical intervention. The doctor performs a curettage by inserting an endoscope through the vagina, which allows you to see the uterine cavity on a computer monitor. Polypectomy plays an important role in the treatment of neoplasms. The procedure not only helps to determine the characteristics of polyps, but also implies the possibility of conducting their surgical treatment. Removal of the polyp in the uterus with a laser ensures complete elimination of the formations, it is carried out in the first phase of the cycle.
Curettage of the polyp in the uterus can have negative consequences:
- fever;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- severe bleeding;
- uterine perforation (puncture of the organ wall);
- inflammation of the female organs.
Video: how to treat a polyp in the uterus
What to do if uterine polyposis is diagnosed? If small polyps are found in the body of the uterus, the symptoms and treatment of which are determined by the doctor, there is no reason to panic. Often, the treatment of small formations is dispensed with without operations and hormonal methods. However, a prerequisite for therapy is the observation of a doctor, implying regular examinations. After watching the video, you will learn what methods of treatment for polyposis exist.

Modern women are not content with the role of a housewife. They are actively engaged in business, participate in public life, travel. But one of the main women's missions remains the birth of children. To experience the joy of motherhood and remain desirable for men, a woman must monitor her health. It is necessary to regularly undergo examination by a gynecologist. This will help in time to detect polyps in the uterus, the symptoms of which may not appear for a long time.
Polyps are a special type of benign neoplasms that are located on the inner walls, in the cavity and cervix. They are formed with the growth of the endometrium (the so-called uterine mucosa). The polyp rests on the leg. Its thickness may be different. Sizes of polyps - from 2-5mm to several centimeters.
Entire groups of tumors can form in the uterus. Sometimes they are found in the cervix. Symptoms of polyp groups are similar to single cases.
Doctors have no consensus on what causes polyps. Factors that can provoke pathological formations are:
- disturbed hormonal balance;
- erosion in the neck;
- inflammation;
- predisposes to the appearance of polyps in the uterus the presence of extra pounds;
- hypertension is also on the list of risk factors.
 During the period of gestation, the hormonal background changes dramatically. Polyps begin to grow rapidly. The same effect is caused by the use of contraceptives containing many synthetic hormones. When the concentration of estrogen in the body decreases, the polyps stop growing. This happens after menopause sets in.
During the period of gestation, the hormonal background changes dramatically. Polyps begin to grow rapidly. The same effect is caused by the use of contraceptives containing many synthetic hormones. When the concentration of estrogen in the body decreases, the polyps stop growing. This happens after menopause sets in.
The reasons that increase the likelihood of polyps in the cervix are hormonal changes that precede menopause.
Polyps grow intensively in women from 40 to 50 years old. Before and after this age they are diagnosed much less often.
What signals the formation of polyps?
What symptoms should cause a woman’s anxiety and suspicion of polyps in the uterus? Often, there are no obvious symptoms of the disease. It can only be detected during a routine inspection.
Among the standard features are the following:

Colonies of polyps do not allow the fertilized egg to stay in the uterine cavity. The reproductive capabilities of a woman are impaired; she cannot conceive a child.
There are other symptoms. If polyps grow in the uterus, then spotty spotting may appear after intimacy. Characteristic symptoms arise due to the fact that the polyp negatively affects the tissue. This entails the exposure of small vessels and causes their bleeding.
 The main symptom that gives an occasion to visit a doctor is vaginal bleeding. Any violations of the normal course of menstruation can indicate the formation of polyps. If a woman has such symptoms, then she should be examined immediately. Timely treatment will help prevent serious oncological diseases.
The main symptom that gives an occasion to visit a doctor is vaginal bleeding. Any violations of the normal course of menstruation can indicate the formation of polyps. If a woman has such symptoms, then she should be examined immediately. Timely treatment will help prevent serious oncological diseases.
Varieties of polyps
The area where polyps usually develop is not limited to the uterine cavity. They are often localized in the neck.
Depending on the structure, polyps can be:
- Glandular. Found in young women. Their basis is glandular tissue.
- Glandular fibrous. They include glandular and connective tissue.
- Fibrous. Connective tissue predominates in their structure. Symptoms characteristic of such a neoplasm, caused by the "presence" of polyps, are detected in older women.
Modern methods for the diagnosis of polyps
A routine gynecological examination does not always guarantee the detection of polyps in the uterine cavity. The doctor can see them only on the neck. It is necessary to use special diagnostic tools.
If symptoms are detected that can be caused by a polyp formed inside the uterus, then a comprehensive diagnosis is necessary. It consists of the following procedures:

Analysis of the obtained samples will help establish the causes and detect atypical polyps. This is important, since such neoplasms on the cervix (or in the uterus) can cause cancer.
How to treat polyps?
Many believe that the polyp does not require treatment, since it is not a malignant formation. But he is one of the causes of infertility. Atypical form in the uterine cavity threatens the onset of cancer.
Some polyps dissolve without assistance. For this, women use folk methods.
In most cases, it is still necessary to resort to medical intervention.
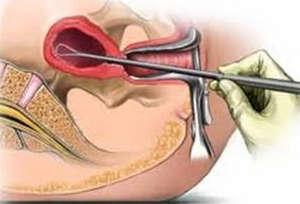 The traditional treatment is to remove these neoplasms. This procedure is called gynecological curettage. It is performed under local or general anesthesia. When surgical treatment is over, the woman may feel unexpressed pain. She is spastic in nature.
The traditional treatment is to remove these neoplasms. This procedure is called gynecological curettage. It is performed under local or general anesthesia. When surgical treatment is over, the woman may feel unexpressed pain. She is spastic in nature.
In the rehabilitation period, which lasts from 1 to 2 weeks, it is not recommended to enter into intimacy.
Hysterectomy
If the number of polyps in the uterus is large, then a treatment called hysterectomy is used. Such treatment is accompanied by local anesthesia (or general anesthesia). This is a safe method that has virtually no complications.
The elimination of polyps by surgical means gives a guaranteed high result. When the polyp is removed, the patient can go home and continue active work.
How effective are folk methods?
If a woman decided to use folk waysto dissolve the polyp, then she needs patience. Alternative treatment lasts a long time. The outcome of such home therapy cannot be predicted in advance. Before starting treatment folk methodsIt is imperative to consult a doctor.
 To get rid of formations in the uterine cavity, garlic is often used. It is grated and spread on cheesecloth (folded in two layers). Then make a swab and insert it into the vagina. Treatment lasts 10 days, then take a week break. The course is repeated three times. If the symptoms of the disease have disappeared, an ultrasound examination is necessary.
To get rid of formations in the uterine cavity, garlic is often used. It is grated and spread on cheesecloth (folded in two layers). Then make a swab and insert it into the vagina. Treatment lasts 10 days, then take a week break. The course is repeated three times. If the symptoms of the disease have disappeared, an ultrasound examination is necessary.
 Pumpkin seed treatment is popular. They are crushed (without frying), mixed with boiled egg yolks. The composition is introduced? tablespoons of vegetable oil. After heating for 20 minutes in a water bath, the mixture is ready for use. These funds are treated for five days.
Pumpkin seed treatment is popular. They are crushed (without frying), mixed with boiled egg yolks. The composition is introduced? tablespoons of vegetable oil. After heating for 20 minutes in a water bath, the mixture is ready for use. These funds are treated for five days.
Other natural components are also suitable for treatment with folk methods: onions, calendula, golden mustache, mummy and propolis.
Improving folk methods is not as safe as it might seem. It is necessary to consider contraindications, as well as an individual reaction to some drugs from the "arsenal" of traditional healers.
To treat or not to treat?
How much treatment is needed? These pathological neoplasms in the cervix do not threaten a woman's life. But the polyp can interfere with the occurrence of pregnancy or provoke its breakdown.
 Polyp tends to grow. Large accumulations of tumors in the cervix negatively affect the work of the reproductive organs. This may also lie in the causes of decreased sexual desire.
Polyp tends to grow. Large accumulations of tumors in the cervix negatively affect the work of the reproductive organs. This may also lie in the causes of decreased sexual desire.
The answer is clear: polyps must be treated. What means should be used to combat the female problem, the doctor must decide.






