What are the symptoms of multiple sclerosis and its modern treatment. Multiple sclerosis in women.
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic neurological disease, which is based on demyelination of nerve fibers. This disease occurs among people quite often, however, its prevalence is the globe not uniform. Thus, the highest incidence rate is recorded in the USA, Canada, Europe, and the lowest in Africa and Asia. It is believed that representatives of the Caucasian race are most at risk of developing the disease. The disease occurs at the age of 16-40 years, the peak incidence falls at thirty years. The morbidity structure is dominated by women.
Often people call forgetfulness, absent-mindedness, especially in the elderly, "senile sclerosis." But these phenomena actually have nothing to do with a disease called multiple sclerosis. This is a serious illness that often leads to disability.
The reasons for the development of the disease
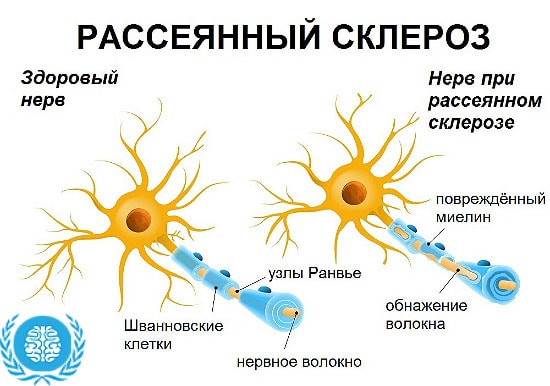
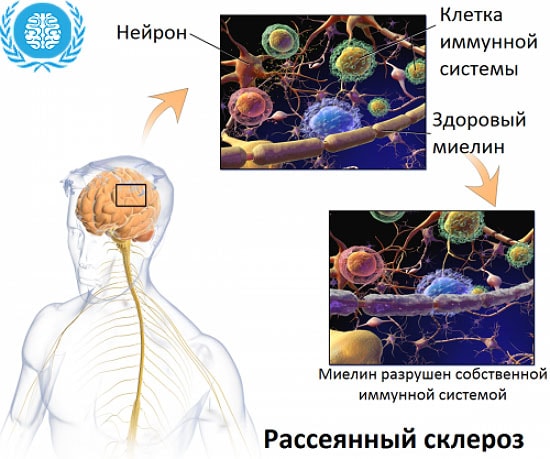
The basic unit of the nervous system is a neuron, which consists of a nucleus, a body and its processes (dendrites and axon). Dendrites are small, branched outgrowths. An axon is a long process with the help of which a nerve impulse is transmitted from a neuron to an executive organ. The axon, in contrast to the dendrite, is covered with a myelin sheath. The quality of the conduction of the nerve impulse will depend on the integrity of the myelin sheath. In multiple sclerosis, it is this sheath that is damaged, as a result of which the affected nerve is unable to fully perform its function.

Why is this happening? Multiple sclerosis belongs to the group autoimmune diseases... That is, the immune system perceives certain cells of the body as foreign (like malignant cells, viruses, bacteria) and begins to fight them. Thus, in multiple sclerosis, T-lymphocytes cross the blood-brain barrier into the brain, where they attack the myelin protein.
As a result of the destruction of myelin (demyelination), sclerotic plaques appear on the surface of the nerve fiber. Plaques are located in the white matter absolutely in any part of the brain or spinal cord, but much more often in the periventricular space of the cerebral hemispheres, trunk, cerebellum, optic nerve junction, somewhat less often in the subcortical structures and the hypothalamus. A patient may simultaneously have plaques at different stages of their development. So, during a relapse of the disease, demyelination processes intensify, new plaques are formed.

The cause of multiple sclerosis is still unclear. It is believed that the precondition for the formation of the disease is the peculiarities of the set of genes that control the immune response. All sorts of external reasons are already superimposed on this factor, which ultimately leads to the development of the disease. TO external factors, provoking the development of the disease, include:

- Oculomotor disorders (, double vision, vertical nystagmus);
- Neuritis of the facial nerve (manifested by peripheral paresis of the muscles of the face);
- Pyramidal disorders (paresis of the extremities, increased tendon reflexes, the appearance of pathological reflexes);
- Cerebellar disorders (staggering while walking, ataxia, intentional tremor (trembling with purposeful movements), horizontal nystagmus, chanted speech, change in handwriting);
- Sensory disorders (numbness, tingling of the skin);
- Dysfunction of the pelvic organs (violation of urination, less often defecation);
- Neurotic disorders (fatigue, emotional lability, depression, euphoria, apathy, intellectual impairment);
- Epileptic seizures.

With multiple sclerosis, a symptom complex occurs, which in medicine is called the "hot bath" syndrome. When taking a bath, the patient's condition worsens. The appearance of this syndrome is explained by the increased sensitivity of the nerve fiber, devoid of myelin, to the effects of environmental factors. Also, there is a syndrome of "inconstancy clinical symptoms", When the severity of symptoms changes not only over the course of months, but even during the day.
The syndrome of "clinical dissociation" is characterized by a discrepancy between the severity of symptoms and the results of a neurological examination. For example, in the presence of an acute decrease in vision and even complete blindness, a normal, unchanged fundus of the eye can be observed.
In most cases, patients have symptoms of damage to both the brain and the spinal cord. This clinical picture is called the cerebrospinal form of multiple sclerosis. If the patient has signs of spinal cord injury, they speak of the spinal form of the disease, and signs of damage to the cerebellum, brain column, optic nerves - of the cerebral form.

In approximately 90% of patients, the disease has an undulating course. This means that periods of exacerbation are followed by remissions. However, after seven to ten years of the disease, secondary progression develops when the condition begins to worsen. In 5-10% of cases, the disease is characterized by a primary progressive course.
Diagnostics
Instrumental research methods make it possible to determine foci of demyelination in the white matter of the brain. The most optimal is the method of the brain and spinal cord, with the help of which it is possible to determine the localization and size of sclerotic foci, as well as their change over time.

In addition, patients undergo an MRI of the brain with the introduction of a contrast agent based on gadolinium. This method makes it possible to verify the degree of maturity of sclerotic foci: active accumulation of the substance occurs in fresh foci. MRI of the brain with contrast allows you to establish the degree of activity of the pathological process.
To diagnose multiple sclerosis, a blood test is performed for the presence of an increased titer of antibodies to neurospecific proteins, in particular to myelin.
In approximately 90% of people with multiple sclerosis, examination of the cerebrospinal fluid reveals oligoclonal immunoglobulins. But we must not forget that the appearance of these markers is observed in other diseases of the nervous system.
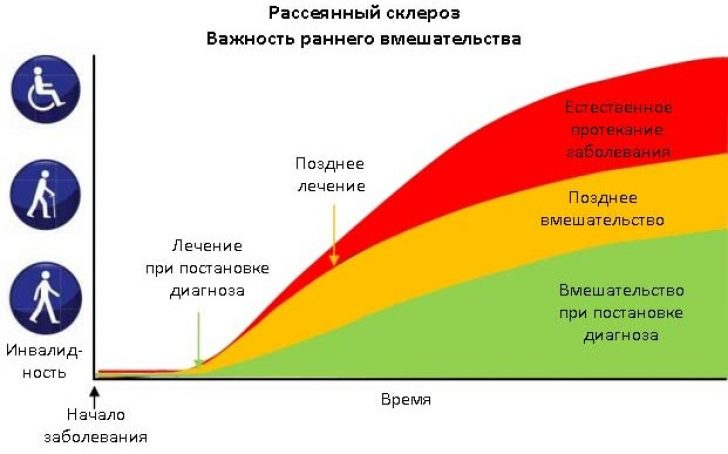
Etiotropic treatment multiple sclerosis has not yet been developed. Therefore, the main direction in the fight against the disease is pathogenetic therapy. There are two directions of pathogenetic therapy: treatment of exacerbation of the disease and inhibition of the progression of multiple sclerosis. Therapeutic tactics should be developed taking into account the characteristics of the clinical course, the activity of the pathological process.

In case of exacerbation of the disease, patients are prescribed glucocorticosteroids. First, pulse therapy is carried out with methylprednisolone - 500-1000 mg of the drug per day is injected intravenously per 400 ml of saline. After a positive result is achieved, usually on the fifth or seventh day, they switch to taking pill corticosteroids, in particular, prednisolone.
To suppress activity immune system use drugs from the group of cytostatics: cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, azathioprine. Taking these medications reduces the severity of exacerbations and also slows the progression of the disease.
A new direction in the therapy of the disease is the use of beta-interferon preparations: Rebif, Betaferon. These drugs have anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and antiviral effects. Beta-interferons are prescribed at 6-12 million IU every other day in a long continuous course. Also in the treatment of multiple sclerosis are used such modern drugs as: Copaxone (Glatiramer acetate), the cytostatic Mitoxantrone, and the monoclonal antibody preparation Natalizumab (Tysabri).
These drugs reduce the number and severity of exacerbations, lengthen the period of remission, and slow down the progression of the pathological process.
Symptomatic treatment is used to relieve specific symptoms of a disease. The following drugs can be used:
- Mydocalm, sirdalud - reduce muscle tone with central paresis;
- Proserin, galantamine - for urination disorder;
- Sibazon, phenazepam - reduce tremor, as well as neurotic symptoms;
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is recognized as more common in women than in men.
This has led to extensive research into differences in immune or nervous system between men and women, which are caused by exposure to gonadal hormones, genetic differences, external influences environment and modern lifestyles in women and men.
In this article we will talk about what multiple sclerosis is, what its symptoms and causes in women.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects movement, sensation, and body function.
It is caused by the breakdown of the myelin isolate that covers nerve fibers (neurons) in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
Description
MS is a nerve disorder caused by the breakdown of the insulating layer that surrounds neurons in the brain and spinal cord. This insulation, called myelin, helps electrical signals travel quickly and smoothly between the brain and the rest of the body. When myelin breaks down, nerve messages are sent out slowly and less efficiently.
Patches of scar tissue, called plaques, form over the affected areas, further disrupting neural connections. MS symptoms occur when the nerves in the brain and spinal cord no longer communicate with other parts of the body. MS causes a wide range of symptoms and affects vision, balance, strength, feelings, coordination, and physical function.
There are approximately 2 million patients in the world. The disease mainly occurs between the ages of 20 and 40.
Symptoms rarely begin before age 20 or after age 60. Women are almost twice as likely to get MS as men, especially in early years... MS rates are higher in the United States, Canada, and Northern Europe than in other parts of the world. MS is rare among Asians, North and South American Indians and Eskimos.
Causes of development and symptoms
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease caused by an attack on the body's own immune system. For unknown reasons, immune cells attack and destroy the myelin sheath, which isolates neurons in the brain and spinal cord. Like the insulation around wires in electrical systems, glial cells form a membrane that surrounds axons called myelin.
Loss of communication between the brain and other parts of the body interferes with the normal flow of sensations and control messages, resulting in MS symptoms. Demyelinated areas appear as plaques, small, circular areas of a gray neuron with no white myelin coating.
Symptom progression in MS correlates with the development of new plaques in the part of the brain or spinal cord that controls the affected area. Since no pattern is observed in the appearance of new plaques, the progression of MS can be unpredictable.
Despite considerable research, the trigger for this autoimmune destruction is still unknown.
The studies being conducted pointed to genes, environmental factors, viruses, or a combination of both. Stress can be a risk factor, although the evidence to support this is weak. Vaccinations have been studied as causal factors. However, most studies show no connection.
The risk of developing the disease is higher if another family member is sick, which indicates the influence of genetic factors. In addition, the higher prevalence of MS among people of northern European descent indicates some genetic susceptibility.
The role of the environmental factor is proposed in studies of the impact of migration on the risk of developing MS. Age is another indicator that is important in determining this risk. One of the interpretations of these studies is that in early age an environmental factor is acquired, both protective and harmful, the risk of disease at a later age reflects the consequences of the early environment.
The same data is used to support a slow-acting virus, which is acquired at an early stage, but begins its destructive effects much later. Slow viruses are known to cause other diseases, including AIDS. In addition, viruses have been implicated in other autoimmune diseases.
It is also unclear how the virus triggers an autoimmune response. There are two main models of virus-induced autoimmunity.
The first suggests that the immune system is actually infecting the virus (too well hidden to detect in the laboratory), and that myelin damage is an unintended consequence of fighting the infection.
The second model suggests that myelin is mistaken by the immune system for a viral protein that it encountered during a previous infection. By forcibly attacking, it destroys myelin because it resembles a previously recognized viral invader.
Any of these models play a role as genetic factors, as some genes increase the likelihood of autoimmune disease. Environmental factors also alter sensitivity.
Symptoms
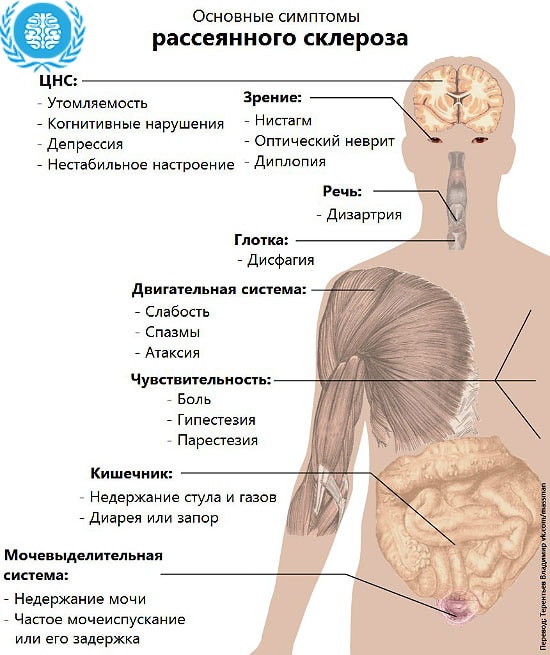
Manifestations are caused by impaired transmission of nerve signals from the central nervous system (CNS) and include:
- fatigue;
- tingling, numbness, or pain;
- difficulty with walking and balance;
- visual impairment;
- depression, emotional changes;
- impaired thinking / understanding;
- poor muscle coordination;
- sexual problems;
- slurred speech and stuttering;
- bowel problems and involuntary urination.
Treatment

Various MS treatment options are available today that have been shown to reduce relapse rates and slow disease progression. Some procedures use injections - subcutaneous or intramuscular, while others are administered intravenously (through infusion) or orally (through the mouth).
Beta-interferons are injectables used to treat relapsing remission MS.
Several interferon-beta products are also used for the first clinical episode with MRI findings consistent with MS. Depending on the drug, interferon beta injections are either subcutaneous or intramuscular, and the dosage ranges from once a day to once a week.
Glatiramer acetate is given by subcutaneous injection every day for the treatment of recurrent remission MS.
Fingolimod is a once-daily oral capsule to treat relapsing forms. Reception reduces the frequency of clinical exacerbations and debugs the accumulation of physical disability.
Teriflunomide is a once daily oral tablet used to treat patients with relapsing forms.
Natalizumab is an intravenous drug intended for patients with rapidly progressing MS or highly active disease despite the use of alternative treatments. It is introduced every four weeks.
Dimethyl fumarate is an oral capsule taken twice a day.
Alternative treatment

Bee venom has been suggested as a treatment, but no research or objective reports support this claim.
In British studies, marijuana has been shown to have variable effects on symptoms.
Improvements have been reported in terms of tremor, pain and spasticity, as well as deterioration in posture and balance. Side effects include weakness, dizziness, relaxation and incoherence, and euphoria. As a result, marijuana is not recommended as an alternative treatment.
Some studies support the value of high doses of vitamins, minerals and others food additives to control the progression of the disease or improve symptoms. Alpha linoleic and linoleic acids, as well as selenium and vitamin E have been shown to be effective in treating MS.
Selenium and vitamin E act as antioxidants. In addition, a Swank diet (low in saturated fat) maintained for an extended period of time can slow the disease process and may help with treatment.
Research has also shown that Tai Chi can be effective in treating MS because it works to improve balance and increase strength.
There are conflicting views on echinacea and its benefits. Some medicine books recommend Echinacea for people with this condition. However, echinacea appears to stimulate various parts of the immune system, especially immune cells known as macrophages. In MS, these cells are very active, and further stimulation can worsen the disease.
Forecast
It is difficult to predict how any person will develop multiple sclerosis. Most people with MS will be able to continue walking and working for many years after their diagnosis.
Fewer than 5% of people with MS are severe, progressive, resulting in death from complications within five years.
On the other hand, 10-20% are benign with very slow or no progression of their symptoms.
The most recent studies show that about seven in 10 people with MS are still alive 25 years after their diagnosis, compared with about nine in 10 people of the same age without disease.
On average, MS will shorten the lives of women by about six years. Suicide is an important cause of death in MS, especially in younger patients.
The degree of disability that a person experiences five years after onset averages about three-quarters of the expected disability after 10-15 years. A favorable course in the first five years usually indicates that the disease will not cause discernible disability.
Planning for birth and the postpartum period in multiple sclerosis.
If a woman with such a disease wants to give birth to a child, there are no contraindications to this. There are all chances, along with healthy ones, the main thing is to consult a doctor and fulfill his requirements.
You should also remember about outbreaks. In the first 9 months after birth, up to 40% of women with MS will relapse. But the outbreak does not increase the risk of long-term disability.
You should think carefully about breastfeeding. If they return to the medication, the woman will not be able to do this. The drugs negatively affect the baby through milk.
Do not feel guilty if you choose a medicine for breastfeeding... After all, your new supplement needs a mom who can stay healthy.
Women with MS are at higher risk for depression during pregnancy and immediately after birth. You can meet a woman who has a positive experience of motherhood and illness. Looking at a positive example, the mood will be more optimistic.
Should I worry if my child will have MS?
This is a problem for parents-to-be.
The disease has some genetic links, but children have a 96% chance that they will benefit.
Output

Autoimmune diseases (mediated by cells or antibodies), including MS, are most common in females. New technologies provide new methods with the ability to further analyze the genetic and immunological mechanisms that cause the observed differences between women and men with MS.
Such studies will require a great collaborative effort, including the careful characterization of standardized detailed clinical characteristics in clinics and countries. As knowledge develops, molecular methodologies can be implemented in clinical practice and influence the selection of the best and personalized screening and treatment for women with MS.
Pregnancy tends to suppress the mother's immune system to prevent rejection of the fetus.
The treatment used during ART can also influence the evolution of multiple sclerosis by altering the patient's hormonal status. It is advisable to discontinue disease-modifying treatment prior to conception.
The use of drugs during conception should be considered on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the risks associated with exposure medicines and the risk of relapse.
There is no known way to prevent multiple sclerosis. Until the cause of the disease is discovered, this is unlikely to change. Good nutrition, adequate rest, avoidance of stress, heat and extreme physical activity, good bladder hygiene can improve quality of life and reduce symptoms.
This disease is susceptible to maintenance. The main thing is not to delay, you need to immediately go to the specialists for examination and drawing up a competent treatment. Subject to treatment and prevention, the life of patients does not differ from healthy ones. People with multiple sclerosis may continue to be active social life and rejoice in the moments.
From how, how the disease manifests itself, from the processes that proceeded during the development of pathology in the myelin sheath at the onset of the disease, when the symptomatology had not yet manifested itself, it is customary to divide into various forms by which the severity of the course of the disease can be determined.
In the case of a benign course, the disease manifests itself big amount attacks, but gradually, the stages of remission of the disease become more and more prolonged. During this time, the myelin sheath is restored, and the symptomatic signs of the disease disappear. People with benign multiple sclerosis can expect long-term remission.
Disease types
Various types of multiple sclerosis are distinguished downstream:
- remitting;
- primarily progressive;
- secondary progressive;
- progressively remitting.
Remitting multiple sclerosis
With this course of the disease, bouts of exacerbation alternate with stages when the patient feels relief. The functionality of the affected areas of the brain in this episode can be restored both completely and partially. The exacerbation stage can last for several months (or maybe several days).
Primarily progressive form
This type of disease is characterized by a slow weakening of the patient's state of health. Primarily progressive multiple sclerosis passes without acute exacerbations, however, as a rule, it leads to complete disability.
Secondary progressive form
At the initial stage, secondary progressive multiple sclerosis in terms of the manifestation and course of the disease is very similar to the remitting form (when there is an alternation of times of deterioration and periods of improvement in health). Then the disease passes into the next form - progressive.
Progressive-remitting form
This type (form) of the disease is the rarest. The remitting course of multiple sclerosis is characterized by the fact that the deterioration in general well-being is constantly progressing, the attacks are repeated very often. The onset of the course of the disease is similar to the primary progressive form.
Multiple sclerosis is classified by form. The disease is classified as follows (it all depends on what exactly, and to what extent, which organ or area in the brain is most affected):
- Cerebral form - the localization of damage is concentrated in the brain.
- Spinal form of multiple sclerosis - lesions are concentrated in the spinal cord.
- The cerebrospinal form for multiple sclerosis of the cerebrospinal form is characterized by a lesion in the two above-mentioned zones at once.
Stages of multiple sclerosis and their symptoms
The onset of multiple sclerosis (this is the second name of this ailment) may not be noticed in the early stages of its development, since its symptoms, as a rule, do not cause concern in patients. On initial stage the symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- loss of energy based on depression or stress;
- household and work chores seem impracticable;
- a slight decrease in intellectual activity;
- severe fatigue.
Often primary symptoms diseases on early stages begin to appear after the postponed, childbirth, operations.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic disease that affects the brain and spinal cord. It is caused by the malfunctioning of the immune system. Its cells invade the brain, destroy the myelin sheath of nerve fibers and lead to scarring. In this case, the nervous tissue is replaced by connective tissue.
Do not confuse multiple sclerosis with senile disease, which we used to call "sclerosis". "Scattered" in this case means that the foci of the disease are, as it were, scattered throughout the entire nervous system. And the word "sclerosis" - describes the nature of the violations. It is sclerosed scar tissue that looks like a plaque. Its sizes range from microscopic to several centimeters.
Multiple sclerosis is a disease that affects young people. Unlike other neurological diseases, which more often occur in old age, this one occurs in people between the ages of 15 and 40. There are cases when MS was found in children from two years of age. But after 50, the risk of getting sick with this ailment decreases sharply.
This disease is quite common. It ranks second for reasons of neurological disability in young people (after injuries). On average, 20-30 cases of the disease are diagnosed per 100 thousand of the population.
There is an interesting pattern: the farther from the equator, the higher the incidence rate. People in the northern regions get sick much more often (70 cases per 100 thousand). This has been attributed to an insufficient amount of vitamin D, which is produced in the human body when exposed to sun rays... Women get sick 2-3 times more often than men. But at the same time, they are easier to tolerate the disease. The disease is not significantly affected.
There is also a connection with race. So the Japanese, Chinese and Koreans are practically unfamiliar with this disease. And most of all Europeans suffer from it. In large cities, the percentage of cases is several times higher than in rural areas. These facts indicate that factors of an unfavorable environment can influence the onset of the disease.
It should be noted that the myelin sheath has the ability to recover independently and under the influence of drugs... Therefore, in those patients whose recovery processes are faster than the formation of plaques, exacerbations can be weak and very rare.
Causes of the disease
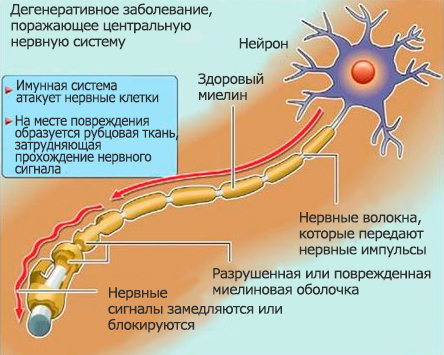 The main cause of multiple sclerosis is a malfunction of the immune system. Normally, the brain and spinal cord are protected by a blood-brain barrier, through which microorganisms and blood cells do not penetrate. In patients, immune cells - lymphocytes - enter the brain. Instead of attacking foreign bodies such as bacteria, they fight the cells of their own body. Lymphocytes produce antibodies that destroy the myelin sheath nerve cells... An area of inflammation arises, at the site of which scar tissue forms. Such plaques on nerve fibers disrupt the conduction of impulses from the brain to the organs. As a result, the brain cannot effectively control the processes and actions of the body. Voluntary movements and speech are hampered, sensitivity decreases.
The main cause of multiple sclerosis is a malfunction of the immune system. Normally, the brain and spinal cord are protected by a blood-brain barrier, through which microorganisms and blood cells do not penetrate. In patients, immune cells - lymphocytes - enter the brain. Instead of attacking foreign bodies such as bacteria, they fight the cells of their own body. Lymphocytes produce antibodies that destroy the myelin sheath nerve cells... An area of inflammation arises, at the site of which scar tissue forms. Such plaques on nerve fibers disrupt the conduction of impulses from the brain to the organs. As a result, the brain cannot effectively control the processes and actions of the body. Voluntary movements and speech are hampered, sensitivity decreases.
There are factors that can trigger the onset of the disease:
- Genetic predisposition - the presence of altered genes
- Severe stress
- Viral and bacterial diseases
- Lack of vitamin D
Some scientists associate the development of the disease with vaccination against hepatitis B. But on this moment there is no confirmation of this theory. There is also an opinion that the disease can be caused by a virus. For example, a mutated measles pathogen. This theory is supported by the fact that with the introduction of antiviral interferons, the patient's condition improves.
Main symptoms and signs
 The disease develops gradually. At the first stages, it does not manifest itself in anything. This is because healthy brain cells take over the function of the affected areas.
The disease develops gradually. At the first stages, it does not manifest itself in anything. This is because healthy brain cells take over the function of the affected areas.
The very first signs appear when about 50% of the nerve fibers are already affected. At this stage of the disease, patients have the following complaints:
- One or two-sided visual impairment
- Pain and
- Feeling of numbness and tingling in the fingers
- Decreased skin sensitivity
- Muscle weakness
- Impaired coordination of movements
Symptoms can vary greatly from patient to patient. Even in one person, they can appear and disappear or be replaced by others.
Over time, as a result of the increase in the number of sclerotic plaques, other signs of the disease appear.
- Spasm and soreness in the muscles.
- Retention of urination and constipation, over time, the patient may lose the ability to control the processes of emptying the bladder and intestines.
- Changes in sex life.
- The appearance of pathological pyramidal reflexes, which do not occur in healthy people. They can only be identified by a neurologist.
- Increased fatigue when performing physical activities.
- Incomplete paralysis of the limbs, difficulty in voluntary movements.
- Paralysis of the cranial nerves: oculomotor, trigeminal, facial, hypoglossal.
- Rhythmic oscillatory movements of the eyeballs.
- Behavioral disorders and decreased intelligence.
- Neuroses, emotional instability, alternation of depression and euphoria.
The condition of many patients temporarily worsens after taking a hot bath, staying in a hot room, during a fever. This must be taken into account and try to avoid overheating, which can provoke an attack.
The course of the disease is characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission, when the symptoms are significantly weakened. Correctly selected treatment can significantly shorten the duration of the exacerbation period and prolong the period of relative health.
Diagnostics
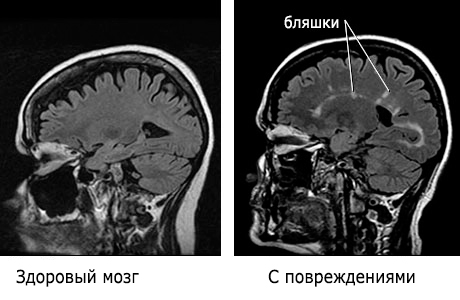 Correct and timely diagnosis makes it possible to provide a sick person with long years full and active life. Therefore, if one or more of the neurological symptoms listed above appear, you should consult a doctor.
Correct and timely diagnosis makes it possible to provide a sick person with long years full and active life. Therefore, if one or more of the neurological symptoms listed above appear, you should consult a doctor.
For differential diagnosis multiple sclerosis, the following factors are important:
- The presence of at least two cases of signs of multiple sclerosis lasting more than 24 hours. The interval between them is about a month.
- When carrying out magnetic resonance imaging, foci of sclerosis - areas of demyelination were noticed.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe an additional examination. For example, an immunological blood test or electromyography.
Prophylaxis
For the prevention of exacerbations in patients with multiple sclerosis, it is recommended:
- Avoid stress and mental fatigue;
- Physical exercise should be regular (playing sports), but not exhausting (read about exercise therapy);
- Give up alcohol and smoking;
- Eat right, do not abuse fatty foods (how to eat right with this disease);
- Normalize your weight;
- Do not overheat;
- Do not use hormonal contraceptives;
- Even during periods of remission (relief of symptoms), take treatment regularly.
Such measures will help reduce the manifestations of illness and prolong periods of health.
Consequences of the disease
In 25% of cases, the disease is benign. Patients remain working for many years and can self-serve. In other cases (10%), disability occurs 5 years after the detection of the disease.
The disease is easier if it started at an early age and has periods of prolonged remission. The first symptom was visual impairment. In this case, one can hope for an easier course of the disease. So, multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease of the nervous system, which is associated with a malfunction of the immune system. At the moment, it is impossible to say exactly what factors cause the onset of the disease. There are many medications that relieve the symptoms of the disease.
The course of the disease is individual for each patient and there is a hope that with correct treatment a person will be able to maintain mental and physical health even in old age.
One of the severe disorders of the nervous system is multiple sclerosis... This disease is characterized by a chronic progressive condition. During examination of the brain and spinal cord, pathological foci are found, the appearance of which has a destructive effect on the sheaths of nerve fibers (myelin).
Specialists call these foci plaques of multiple sclerosis. Usually these plaques are small in size. But there is a tendency to increase and combine them.
It is believed that young people and even children are more likely to get sick. However, this disease can also occur in old age.
Causes
Pathology is based on viral infection(measles, mumps, rubella, herpes). These viruses destroy the cell and myelin, which is the protein sheath of nerve fibers. In their place, a foreign protein is formed - a prion. In response to the appearance of these unfamiliar elements, the lymphocytes begin to produce antibodies. The fight begins with the body's own cells, and not with the virus.
The immune system begins to malfunction. This leads to an autoimmune reaction. In this condition, the nervous system is suppressed by its own defenses. Inflammatory foci of myelin destruction are formed in the brain and spinal cord. The location of these foci is scattered, and they can have a different age of formation.
There are three stages.
- an acute stage that has arisen recently;
- foci that have arisen a long time ago, and they may be in an inactive form;
- chronic foci lead both to a latent course of the disease and to an active form. In any phase, the destruction of the white matter occurs.
In multiple sclerosis, not only white matter, but also gray matter (the body of nerve cells), as well as nerve fibers, are destroyed. The decay process takes place gradually. Slow wear continues not only in the acute stage, but also during the abatement of symptoms, when a visible calm is created.
Among the factors provoking this disease, several can be distinguished.
- there are more young people who have the disease;
- female;
- various diseases of the psyche and emotional sphere of a person;
- infectious pathologies, viral or bacterial origin;
- problems in the functioning of blood vessels;
- hereditary factor;
- radiation radiation.

Autoimmune diseases can also be a triggering factor. The list of such diseases is very long. One organ or an entire system may suffer. Systemic ailments include, for example, lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis. The defeat of individual organs can also affect the functioning of the body as a whole. These diseases include, for example, cirrhosis of the liver, myocarditis. Endocrine diseases: diabetes, pathology of the thyroid gland.
Course of the disease
The ailment in question can occur in different form depending on the severity.
- mild course of the disease is characterized by minor symptoms and long periods of remission;
- multiple sclerosis of moderate severity, when the symptoms intensify, and the stages of remission are shortened with each subsequent active phase;
- severe progressive condition.
Allocate several forms this disease, which differ in the prevailing symptoms of the patient. Cerebral and spinal forms, cerebrospinal, atypical, ocular, hyperkinetic. The atypical form of multiple sclerosis includes Marburg disease. This disease belongs to the class of malignant tumors. The disease makes itself felt at a young age. It passes sharply, without subsiding.
The main symptoms are partial or complete paralysis of four limbs, bulbar syndrome: impaired speech, breathing, swallowing, impaired consciousness, (lack of speech)
The disease cannot be completely cured and leads to disability. When a person's symptoms do not subside, and there are no stages of remission. Sometimes, when respiratory and cardiac activity is affected, a person cannot cope with the disease and dies. In most patients, higher nervous activity at the initial stages of the disease is not affected or suffers minimally.
A person is able to solve problems, run a household, communicate. But he has great fatigue, which deprives him of activity. An important feature is that the nervous system suffers, due to the detachment from society. The patient is not allowed to do his usual business.
Arise nervous disorders, as a result of lack of demand. A person is in a constant state of stress, falls into depression. On how much a person experiences and perceives the current situation, his physical condition depends.
Symptoms
After the destruction of the myelin sheath, transmission is impaired nerve impulses... Demyelination can occur anywhere, resulting in neurological disorders. During the illness, stages of exacerbation alternate with stages of remission. If the disease is detected for the first time, then neurological problems may not be traced.
During the next exacerbation, neurological signs may intensify or be supplemented by new disorders. What pathologies arise depends on the place where the demyelination occurred, as well as on the importance of the nerve segment in the functioning of the body as a whole. Localization sites of destruction are in a chaotic manner throughout the nervous system. There can be many of them.
Some people may have mild symptoms. A comprehensive examination by all doctors will make it possible to recognize this disease.
The person himself may also notice behavioral disturbances.
- violation of body coordination, and coordination suffers not only during movement, but in a static position;
- tremor of the limbs;
- sensory disturbances (a person may feel tingling or numbness in certain parts of the body).
It happens that a person, for several years after the first exacerbation, does not meet with symptoms of the disease. But this does not mean that it has disappeared. The active stage will still arise. This stage is characterized by more pronounced symptoms.
- most often pathologies of motor functions are traced: paresis, paralysis, paresis of the muscles of the limbs, a feeling of tension in the muscles of the arms and legs;
- hyperkinesis - involuntary movement in various muscle groups: tremor, dystonia;
- optic neuritis, visual acuity is impaired, sometimes complete blindness can be traced, a film may appear before the eyes;
- stem and cerebellar symptoms, double vision, dizziness with nausea, staggering during movement, awkwardness of the hands;
- some reflexes disappear;
- sphincter symptoms, any urinary disturbances;
- mental disorders (asthenia, depression, neurosis);
- dysarthria - a speech disorder, consisting in the difficulty of reproducing individual words, sounds;
distortion of taste; - weakness of the muscles of the face: twisting of the cheeks, the eyelids do not close.
These violations can periodically disappear, then return again.
Symptom complexes
Multiple sclerosis is characterized by a number of symptom complexes.
- The syndrome of "clinical inadequacy" is that a person does not feel the objective symptoms of the pathways. For example, during the examination, a violation of the muscle tone in the legs was found, but the patient can perfectly move over long distances.
- The syndrome of "inconsistency of clinical symptoms." The patient's existing symptoms can change not only during years but even during the day. The severity of one symptom may decrease or increase.
- Feelings of heat in the body, "hot bath syndrome". The patient begins to feel worse when the ambient temperature rises. For example, even after hot meals.
Clinical manifestations
There are two groups of symptoms of multiple sclerosis: classic and rare.
Among the main clinical manifestations, there are several.
- The defeat of the pyramidal pathways leads to hemiparesis or paraparesis. Sudden mood swings occur. Loss of abdominal cutaneous reflexes, changes in muscle tone.
- Violation of the cranial nerves. For example, damage to the facial nerve leads to a violation of the sensitivity of half of the face.
- Violation of sensitivity. The patient complains of numbness, burning, tingling in various parts of the body. No touch is felt in any particular area.
- Dysfunction of the pelvic organs leads, for example, to incontinence or urinary retention.
- Change in intelligence. Excessive emotionality appears, a violation of the cognitive sphere of a person. Attention, memory, thinking, imagination suffer.
Diagnostics
Symptoms are so subtle that they can be attributed to any other medical condition. Therefore, only a deep, instrumental examination in the clinic is necessary.
The patient is under the supervision of a cardiologist, neuropathologist, ophthalmologist, immunologist, urologist.
- magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and spinal cord;
- evoked brain potentials (during this examination, electrical impulses are recorded that enter the brain from the sense organs);
- the study of cerebrospinal fluid and blood, for example, in multiple sclerosis, gamma globulins increase in the cerebrospinal fluid.
- treatment aimed at slowing the development of the disease;
- treatment aimed at reducing the stage of exacerbation;
- treatment of the symptoms shown;
- preventive treatment to increase the stage of remission;
- measures aimed at adapting the patient to the consequences of the exacerbation stage in order to make life easier.
Treatment
The prognosis of the disease depends on the age of the patient and on the number of symptoms shown. Later, the disease is less dangerous to health and life. Availability a large number manifestations of the disease complicates the course of treatment. Treatment is carried out in several directions.
Pathogenetic therapy
During an exacerbation of the disease, several methods of dealing with the disease are distinguished.
- The main one is hormonal therapy, which is carried out in short courses, but the dose is maximum. The earlier treatment is started, the more effective the anti-inflammatory effect will be. Together with similar drugs, they give drugs that protect the gastric mucosa, vitamin complex, preparations containing potassium and magnesium.
- Plasmapheresis. The essence of the procedure is to safely cleanse the blood at the cellular level using special devices.
- Cytostatics. They inhibit abnormal cell reproduction or completely eliminate it.
- B-interferons are immunomodulators that allow you to fight viruses and slow down the progression of the disease.
Symptomatic therapy
- Antioxidants They are able to cleanse the body of harmful molecules.
- Nootropics have a beneficial effect on the functioning of the entire brain. Cognitive processes are improved, the intellectual sphere is stimulated.
- Amino acids. They help the body recover from illness faster. Increases immunity.
- Vitamin complexes.
- Anticholinesterase drugs. Their therapeutic effect is to inhibit the activity of cholinesterase. These drugs increase the contraction of the smooth muscles of the eyes, bronchi and other organs. Helps with enuresis.
- Vascular therapy is aimed at cleansing blood vessels and activating their activity.
- Muscle relaxants. They relieve muscle tension, relieve pain. Trembling limbs, awkwardness of movement.
- Enterosorbents. They take out of the blood and gastrointestinal tract harmful substances that have arisen due to pathological processes in this disease.
- Antidepressants, sedatives.
- Antihistamines are used, for example, for frequent dizziness.
This disease is completely incurable. Comprehensive treatment will help reduce symptoms and prolong the stages of remission.
Prophylaxis
No one is immune from multiple sclerosis. You can try to protect yourself from its occurrence. This does not need to be allowed infectious diseases, avoid stressful situations, especially long-term ones, completely abandon bad habits.
Most often, people who already have multiple sclerosis need prevention. Immunomodulators are prescribed that can reduce the manifestation of symptoms and increase the intervals between exacerbations. These injections accompany the patient throughout his life.
The doctor selects a treatment regimen: either daily injections, or every other day, or maybe even less often. Multiple sclerosis is a serious, serious illness that requires responsible, time-consuming treatment. Everyone who surrounds the patient should have patience and strength in order to endure as best as possible all the difficulties associated with this disease.
Video on the topic: Causes, signs, symptoms of multiple sclerosis. Diagnosis and treatment, explains neurologist, immunologist K. A. Shlyapnikov






